Oil & Gas fired Boiler
Oil & gas-fired boilers are robust and efficient heating systems widely used in various industrial applications. These boilers play a crucial role in providing heat and hot water for processes such as manufacturing, refining, chemical processing, and power generation.
Typically designed for high-capacity heating demands, oil and gas-fired industrial boilers are engineered to deliver reliable performance under demanding conditions. They are equipped with advanced combustion systems and controls to ensure efficient fuel utilization and compliance with environmental regulations.
Types
Unsure how to choose a Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler?
Contact us for complimentary boiler selection guidance, cost estimations, and expert technical advice for your project.
Featured
Oil and gas-fired industrial boilers are known for their high thermal efficiency, rapid heating response, and low emissions. They are often integrated into industrial facilities to provide essential heating and steam for production processes, space heating, and other industrial applications.
Due to their reliability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, oil and gas-fired industrial boilers are indispensable components of many industrial operations, helping to ensure consistent and efficient operation across a wide range of industries.
Robust & Efficient
Oil and gas-fired industrial boilers are robust and efficient heating systems widely used in various industrial applications. These boilers play a crucial role in providing heat and hot water for processes such as manufacturing, refining, chemical processing, and power generation.
A variety of configurations
In industrial settings, oil and gas-fired boilers come in a variety of configurations, including fire-tube, water-tube, and combination boilers, tailored to meet specific process requirements. They are capable of producing steam, hot water, or thermal oil, depending on the application.
Reliable performance under demanding conditions
In industrial settings, oil and gas-fired boilers come in a variety of configurations, including fire-tube, water-tube, and combination boilers, tailored to meet specific process requirements. They are capable of producing steam, hot water, or thermal oil, depending on the application.
High thermal efficiency, rapid heating response, and low emissions.
Oil and gas-fired industrial boilers are known for their high thermal efficiency, rapid heating response, and low emissions. They are often integrated into industrial facilities to provide essential heating and steam for production processes, space heating, and other industrial applications.
Why Choose Taishan Group ?
Leading coal, biomass and waste to energy solution provider.
- Covering Entire Project Lifecycle A-Z Service.
- Ranked top in China's industrial boiler industry for 10 consecutive years.
- Access cutting-edge, eco-friendly energy solutions.
- Benefit from over 70 years of technical expertise.
- Align with global sustainability initiatives.
- China largest-capacity biomass power generation boiler.
- Experience reliable, efficient equipment for green development.
378000+
Workshop m²
5000+
Trained Staff
1978
History Since
Project Case
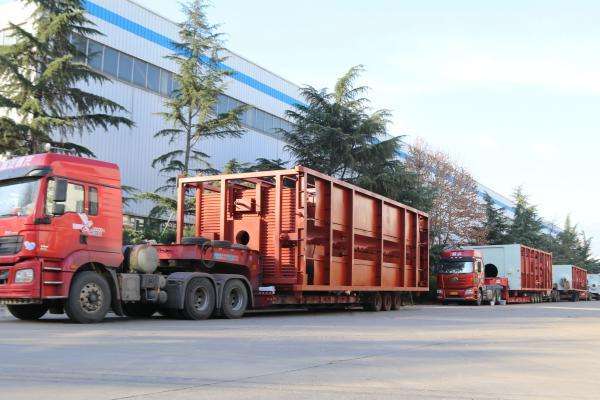

4 sets 60-ton & 2 sets 55-ton gas-fired steam boilers for China Nuclear Engineering Corporation (CNEC) CNEC is one of the leading companies in China's nuclear power engineering construction and operation.

Provide 25t/h supplementary steam for 25MW steam turbine unit for NUH power generation, NUH Cement Plant is the largest port-type cement plant in Turkey.

Provide five 58MW gas boiler boiler bodies and all auxiliary equipment for the boiler island. Beijing Heat Group Co., Ltd. Beijing Heat Group is the primary heating service provider in Beijing, responsible for providing centralized heating services to a majority of buildings and residents in the city.
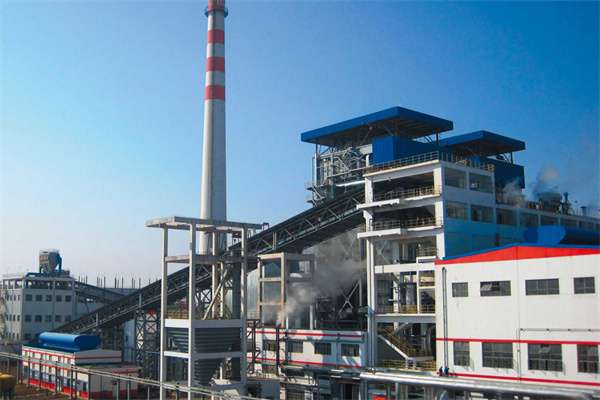

2 sets 170t/h Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler for Vietnam National Coal and Mineral Industries Group Bauxite-Alumina Project
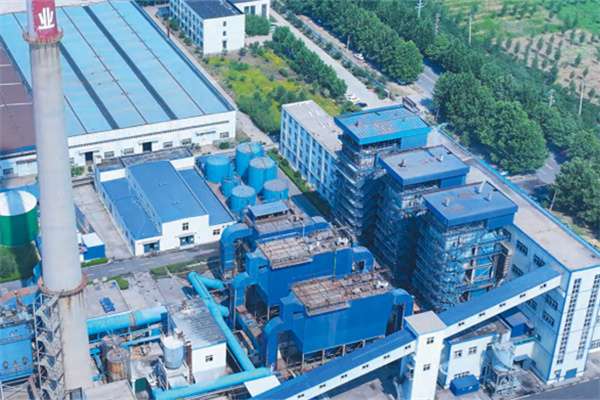

2 sets 20 tons fluidized bed boiler EPC project in Vietnam for Shandong Daiyue Salt Manufacturing in Vietnam
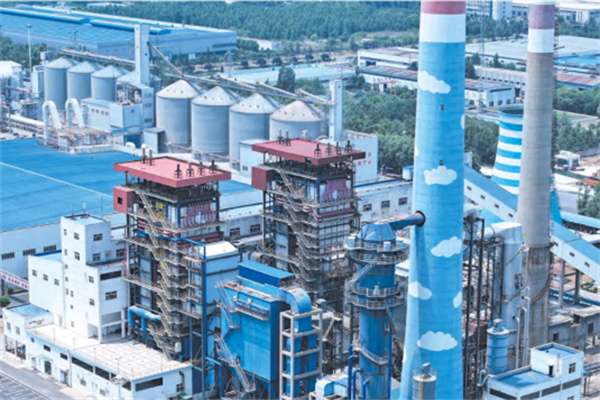

35 tons and 75 tons fluidized bed boiler EPC project for Shandong Fukuan Biological Engineering (Vietnam)
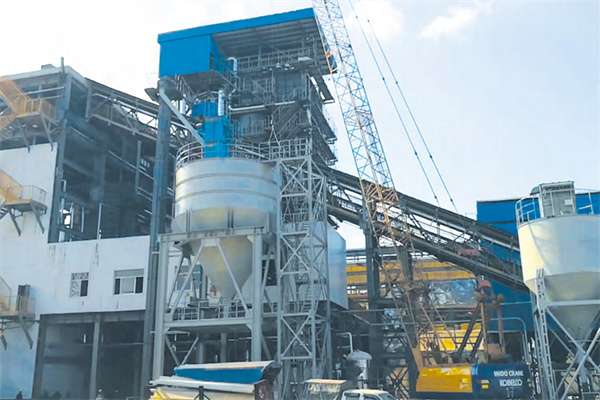

2 sets 116MW Coal CFB hot water boilers for Aksu Sunshine Thermal Company heating projects

2*20 tons fluidized bed boiler in Jinyu Tyre Vietnam EPC project
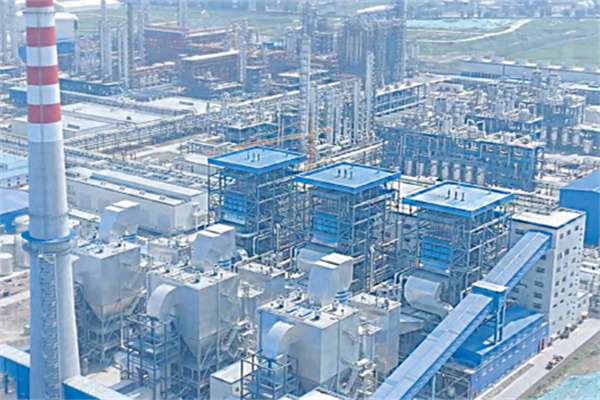

75t/h Coal CFB Boiler for Indonesia PT QMB NEW ENERGY MATERIALSPt Laterite Nickel Ore Smelting Project
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions about Oil & Gas fired Boiler.
An Oil & Gas fired boiler is a type of boiler that uses oil or gas as its fuel source. The basic operation of these boilers is similar to that of any other boiler type, where the fuel is combusted to heat water and produce steam or hot water for heating and industrial processes.
Oil & Gas fired boilers are crucial in residential heating, industrial processes, and power generation, offering a reliable and efficient source of heat when operated and maintained properly.
The operating costs of oil and gas-fired boilers can vary significantly based on several factors, making them more or less expensive to run in different contexts. Here are the key considerations:
1. Fuel Prices
– The cost of oil and gas fluctuates based on global market conditions, regional availability, and geopolitical factors. Generally, when fuel prices are high, the operating costs of these boilers increase correspondingly.
2. Efficiency
– The efficiency of a boiler determines how much fuel is converted into usable heat. Modern high-efficiency boilers can achieve efficiencies of 90% or more, meaning less fuel is wasted. Older or poorly maintained units may have significantly lower efficiencies, leading to higher fuel consumption and operating costs.
3. Boiler Size and Load
– Oversized or undersized boilers for the specific needs of a building or process can lead to inefficiencies. Additionally, boilers that frequently operate at partial load (not at full capacity) can be less efficient than those running at full load.
4. Maintenance
– Regular maintenance is essential for keeping a boiler running efficiently. Neglected boilers can face issues like scaling, soot buildup, and inefficient combustion, all of which can increase fuel consumption and operating costs.
5. Type of Fuel
– The choice between oil and gas can also affect operating costs, as these fuels typically have different prices. In many regions, natural gas is cheaper than oil, though this is not universally the case.
6. Environmental Regulations
– In some regions, there may be taxes or levies on certain fuels or emissions, which can affect the overall cost of running an oil or gas-fired boiler.
Comparison with Other Heating Options:
– When compared to electric heat pumps, oil and gas boilers may have higher operational costs due to the cost of fuel. However, they are often preferred in areas where the electricity supply is unreliable or where electricity prices are high.
– Compared to renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, which have lower operational costs once installed, oil and gas boilers have ongoing fuel expenses. However, boilers can provide consistent heating without reliance on weather conditions.
In conclusion, while oil and gas-fired boilers can be more expensive to run than some alternatives, especially during periods of high fuel prices, their actual operating costs depend on a variety of factors. Efficiency improvements, proper sizing, and regular maintenance can help mitigate these costs. For many applications, especially where high-temperature heat or steam is required, they remain a practical and reliable choice.
Oil and gas-fired boilers offer several advantages that make them popular choices for residential, commercial, and industrial heating requirements. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. High Energy Efficiency
– Modern oil and gas boilers are designed to achieve high levels of energy efficiency, often exceeding 90%. This means that a greater portion of the fuel used is converted into usable heat, reducing fuel consumption and lowering operating costs.
2. Reliability and Availability
– These boilers are known for their reliability and consistent performance. Oil and gas are widely available fuels in many regions, ensuring that these heating systems can be operated without interruption due to fuel scarcity.
3. Versatility
– Oil and gas-fired boilers can be used in a variety of applications, from small residential heating systems to large industrial processes that require steam or hot water. They can be designed to meet the specific needs of almost any application, including adjustable heat outputs and pressures.
4. Rapid Heating
– These boilers can produce heat very quickly from the time of ignition, making them ideal for situations where heat is needed on demand. This rapid response is particularly beneficial in industrial processes and residential heating during cold weather.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
– In regions where oil and gas prices are competitive, these boilers can be a cost-effective solution for heating. Initial installation costs can be higher than some alternatives, but the high efficiency and reliability of modern boilers can lead to lower overall operating costs.
6. Ease of Installation and Maintenance
– Oil and gas-fired boilers have been in use for many years, which has led to well-established standards for their installation and maintenance. A wide network of experienced service providers is available, making maintenance and repair services readily accessible.
7. Compatibility with Existing Systems
– Many existing heating systems are designed to be compatible with oil and gas-fired boilers, making them a straightforward choice for upgrades or replacements without the need for extensive modifications to heating distribution systems.
8. Environmental Options
– Newer models of oil and gas boilers are designed to be more environmentally friendly, with options for condensing technology that captures and reuses heat from exhaust gases, further improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
9. Scalability
– These boilers can be scaled up to meet the needs of large industrial facilities or scaled down for residential use, providing a flexible solution that can be tailored to the specific requirements of the user.
While oil and gas-fired boilers present these advantages, it’s important to also consider environmental impacts and the potential for fluctuating fuel prices. However, for many applications, the benefits of reliability, efficiency, and versatility make them a preferred choice.
While oil and gas-fired boilers offer several advantages, they also come with a set of disadvantages that are important to consider. Here are some of the key drawbacks:
1. Environmental Impact
– The combustion of oil and gas releases carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Other emissions can include nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter, which have various environmental and health impacts.
2. Fluctuating Fuel Prices
– The cost of oil and gas can vary significantly over time due to geopolitical events, changes in demand, and other factors. This can make the operating costs of oil and gas boilers unpredictable and potentially high.
3. Fuel Storage
– Oil-fired boilers require on-site storage of oil, which can pose a risk of spills or leaks. This requires careful management and can add to the overall footprint of the heating system.
4. Infrastructure and Supply Concerns
– Natural gas-fired boilers depend on the availability of a gas supply network, which may not be available in all areas. For oil, regular deliveries must be scheduled, and storage capacity needs to be managed.
5. Maintenance and Cleaning
– Oil and gas boilers require regular maintenance to operate efficiently and safely. This includes cleaning to remove soot and other residues that can accumulate and reduce efficiency. Maintenance and repair can add to the overall cost of operation.
6. Installation Costs
– The initial installation cost of an oil or gas boiler can be high, especially for systems that require extensive ductwork or piping. This can be a significant investment for homeowners or businesses.
7. Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
– In some regions, there are strict regulations regarding the installation and operation of oil and gas boilers due to their emissions. Compliance with these regulations can add to the cost and complexity of using these systems.
8. Long-Term Sustainability
– As the world moves towards cleaner energy sources, the long-term sustainability of relying on fossil fuels for heating is questionable. Investments in oil and gas boilers may face obsolescence as renewable energy technologies become more prevalent and affordable.
9. Space Requirements
– Boilers and their associated fuel storage can take up considerable space, which may be a limitation in densely populated areas or for facilities with limited available space.
Despite these disadvantages, oil and gas boilers remain a common choice for heating due to their reliability, efficiency, and the existing infrastructure in many places. However, the growing emphasis on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality is leading to increased interest in alternative, more sustainable heating solutions.
The lifespan of an oil or gas-fired boiler can vary based on several factors, including the quality of the boiler, maintenance practices, and the intensity of its use. On average, you can expect a well-maintained oil or gas boiler to last between 15 to 30 years.
Key Factors Influencing Boiler Lifespan:
1. Quality of the Boiler:
– Higher quality boilers are typically built with better materials and engineering designs, which can extend their useful life.
2. Regular Maintenance:
– Regular servicing is crucial for maximizing the lifespan of a boiler. This includes tasks such as cleaning, checking for leaks, ensuring that the combustion process is efficient, and replacing worn parts. Proper maintenance can prevent small issues from turning into bigger problems that might shorten the boiler’s lifespan.
3. Operating Conditions:
– Boilers that operate under constant high demand or in harsh conditions may experience more wear and tear, potentially reducing their lifespan. Conversely, boilers operating under moderate conditions with periodic breaks tend to last longer.
4. Water Quality:
– The quality of water used in the boiler can have a significant impact on its lifespan. Hard water, which is high in minerals, can lead to scale buildup inside the boiler’s heat exchanger, reducing efficiency and potentially causing overheating and failure.
5. Installation:
– Proper installation by a professional is crucial for the longevity of a boiler. Incorrect installation can lead to operational issues and increased wear over time.
Signs It’s Time to Replace Your Boiler:
– Frequent Breakdowns: Regularly occurring issues might indicate that the boiler is nearing the end of its useful life.
– Increasing Energy Bills: If your energy costs are rising despite regular maintenance, it could be a sign that your boiler is losing efficiency.
– Difficulty Finding Replacement Parts: As boilers age, it can become harder to find parts, which can be a sign that it’s time for an upgrade.
– Visible Wear or Damage: Signs of rusting, leaks, or damage to the boiler itself or to the surrounding infrastructure can indicate that replacement is necessary.
While the average lifespan provides a general guideline, the actual longevity of a boiler will depend on the specific circumstances of its use and care. Investing in a high-quality boiler and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule are the best ways to ensure that you get the most years out of your investment.
Oil and gas-fired boilers are versatile and widely used across various sectors of industry due to their efficiency and capacity to provide high-pressure steam and hot water. Here are some of the key industries where these boilers play a crucial role:
1. Power Generation
– Used in power plants for generating steam that drives turbines to produce electricity. While coal-fired power plants are more common, oil and gas boilers are used in areas where those fuels are more readily available or as backup systems.
2. Manufacturing
– Essential in industries that require large amounts of steam or hot water for their processes, such as chemical manufacturing, food processing, textile, and paper manufacturing. They are used for heating, drying, sterilization, and in chemical reactions that require steam.
3. Petrochemical and Refineries
– Refineries use these boilers to generate steam and heat for distillation, cracking, and other processes critical in transforming crude oil into usable products like gasoline, diesel, and other chemicals.
4. Pharmaceuticals
– In the pharmaceutical industry, precise control of temperature and clean steam is crucial for the manufacturing of medications, sterilization of equipment, and other processes where contamination must be avoided.
5. Healthcare
– Hospitals and healthcare facilities use steam generated from boilers for sterilization of instruments, laundry, food service, and for creating a controlled environment in terms of humidity and temperature.
6. Hospitality and Commercial
– Large hotels, resorts, and commercial buildings utilize boilers for space heating, hot water supply, cooking, and laundry services.
7. Maritime
– Ships and offshore platforms use oil and gas-fired boilers for heating, propulsion, and power generation, especially in areas where other fuel types are not viable.
8. Agriculture
– Used for heating in greenhouses, processing of farm products, and in some cases, for irrigation through steam-powered equipment.
Advantages in Industrial Use:
– **Flexibility and Scalability:** These boilers can be scaled up to produce large amounts of steam or hot water as per industrial requirements.
– Efficiency: Modern designs and technologies have made oil and gas boilers more efficient, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
– Reliability: They offer a reliable heat source, critical for continuous industrial operations.
Challenges:
– Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations are pushing industries to adopt cleaner energy sources or to invest in emissions-reducing technologies for their boilers.
– Fuel Volatility: Fluctuations in oil and gas prices can significantly affect operational costs.
Despite these challenges, the efficiency, availability, and technological advancements in oil and gas-fired boilers continue to make them a preferred choice in many industrial applications.
Selecting the right oil or gas-fired boiler for your industrial application requires careful consideration of several factors. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps to guide you:
1. Assess Your Heating Needs:
- Heat Output: Determine the amount of heat required for your specific industrial processes. This will help size the boiler appropriately to avoid inefficiencies from an underpowered or oversized unit. A qualified HVAC professional can help you with this assessment.
- Fuel Availability and Cost: Consider the availability and pricing of natural gas compared to oil in your region. While gas is generally cheaper, oil might be the only option in some areas.
2. Boiler Efficiency:
- AFUE Rating: Look for boilers with a high Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating. This indicates the percentage of fuel converted into usable heat, with higher ratings signifying better efficiency and lower operating costs. Condensing boilers, both gas and oil-fired, can achieve AFUE ratings exceeding 90%.
3. Boiler Type:
- Cast Iron Boilers: These traditional boilers are known for durability and can last over 30 years with proper care. However, they tend to be less efficient than newer models.
- Condensing Boilers: These high-efficiency boilers capture additional heat from exhaust fumes, leading to significant energy savings. They are a good choice for facilities with continuous heating demands.
- Hot Water vs. Steam Boilers: Hot water boilers are more common for most industrial applications due to their efficient heat transfer and safety features. Steam boilers might be suitable for specific high-temperature processes.
4. Additional Considerations:
- Maintenance Needs: Oil-fired boilers generally require more frequent maintenance compared to gas-fired models due to potential issues with the oil itself. Factor in maintenance costs when comparing options.
- Fuel Storage: If opting for an oil-fired boiler, consider the cost and space requirements for installing a dedicated oil storage tank.
- Environmental Regulations: Ensure the chosen boiler meets local regulations regarding emissions and environmental impact.
5. Consult a Professional:
- Our experienced professional can help you evaluate your heating needs, recommend suitable boiler options based on your requirements, and provide insights on factors like installation and maintenance considerations.
By following these steps and consulting with our professional, you can make an informed decision when choosing an oil or gas-fired boiler that meets your industrial heating needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
The cost of oil and gas-fired industrial boilers can significantly vary depending on a wide range of factors, including the boiler’s capacity, efficiency, design, and the specific requirements of the industrial process it will serve. Unlike residential boilers, industrial boilers are designed to handle much larger volumes of water and produce higher pressures and temperatures of steam, which can significantly influence their cost.
Initial Purchase Cost
– Small to Medium Capacity Boilers: For smaller industrial applications, costs can range from $10,000 to $50,000. These boilers typically have lower capacities and are suited for light manufacturing processes, small facilities, or as backup units.
– Large Capacity Boilers: For larger industrial operations, prices can start from $50,000 and can go up to several hundred thousand dollars for high-capacity, high-efficiency units that are essential for heavy manufacturing processes, large facilities, or power generation.
Factors Influencing Cost
– Capacity and Output: Industrial boilers are often customized to meet specific steam or hot water requirements, with higher capacities leading to higher costs.
– Efficiency: High-efficiency boilers, especially those designed to recover heat or to operate under condensing conditions, are more expensive but can lead to significant fuel savings over time.
– Design and Type: The design (fire tube vs. water tube), type (steam vs. hot water), and fuel flexibility can affect the price. Specialized designs for specific industrial processes can also increase costs.
– Installation and Setup: Installation costs for industrial boilers can be significant, including the setup of the boiler, integration into existing systems, construction of any necessary infrastructure like flue gas stacks, and compliance with environmental regulations.
– Operational Environment: Boilers designed to operate in harsh conditions or to handle corrosive or unusual fuels can be more expensive due to the need for specialized materials and designs.
– Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with emissions and safety regulations can add to the cost, requiring additional control systems and safety features.
Additional Costs
– Maintenance and Operation: Industrial boilers require regular maintenance to operate efficiently and safely. The complexity of the boiler and the quality of water used can influence maintenance costs.
– Fuel Storage and Handling: For oil-fired boilers, or gas-fired boilers in areas without a direct gas line, the cost for fuel storage and handling infrastructure needs to be considered.
– Energy Costs: The choice of fuel and the efficiency of the boiler will directly impact ongoing energy costs, which can be a significant part of the total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
Given the broad range of industrial applications and boiler specifications, obtaining a precise cost without specific details is challenging. For a detailed and accurate estimate, consultation with manufacturers or suppliers who can tailor a solution to the specific needs of the industrial process is essential. These professionals can provide comprehensive quotes that include the boiler, installation, and any additional components or services required.
Choosing between oil & gas-fired boilers and coal-fired boilers depends on several factors including environmental impact, cost, efficiency, and application requirements. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages based on these criteria. Here’s a comparison to help determine which might be better for specific needs:
Environmental Impact
– Oil & Gas Boilers: Produce fewer emissions compared to coal. Natural gas, in particular, burns cleaner than oil and coal, with significantly lower levels of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter.
– Coal Boilers: Generally have a higher environmental impact due to the higher carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and other pollutants like SO2 and mercury. However, modern coal-fired boilers equipped with advanced emission control technologies can mitigate some of these effects.
Cost
– Oil & Gas Boilers: Operational costs can fluctuate based on the volatile prices of oil and gas. However, these boilers tend to have lower upfront costs compared to coal boilers equipped with advanced emission controls.
– Coal Boilers: Coal typically offers lower fuel costs, especially in regions with easy access to coal supplies. However, the initial investment might be higher due to the need for emission control systems and more complex fuel handling equipment.
Efficiency
– Oil & Gas Boilers: Tend to be more efficient than coal boilers. Modern gas-fired boilers can achieve efficiencies above 90%.
– Coal Boilers: Historically less efficient, but advancements in technology have improved the efficiency of new coal-fired boilers. However, achieving high efficiency often requires additional systems like superheaters, which can increase costs.
Application Requirements
– Oil & Gas Boilers:Are more versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, from residential heating to large industrial processes. They are easier to operate and require less space.
– Coal Boilers: Are often used in industrial applications and power generation where high heat output is needed. They require more space for the boiler itself and for coal storage and handling.
Maintenance and Operation
– Oil & Gas Boilers: Generally require less maintenance than coal boilers, as they do not produce ash and have fewer soot and slag problems.
– Coal Boilers: Require more intensive maintenance due to ash production and the need for regular cleaning to maintain efficiency and operation.
Availability
– The availability of fuel can also be a determining factor. Regions with easy access to natural gas or oil may find that oil & gas boilers are more practical, while areas with abundant coal supplies might prefer coal boilers.
Conclusion
The choice between oil & gas-fired boilers and coal-fired boilers depends on the specific needs of the application, environmental regulations, fuel availability, and cost considerations. For residential and light commercial applications, oil & gas boilers are often preferred due to their efficiency, lower environmental impact, and ease of use. For industrial applications or in regions with low-cost coal, coal-fired boilers might be more economical, especially if equipped with modern pollution control technologies. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a comprehensive analysis of total operating costs, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance.
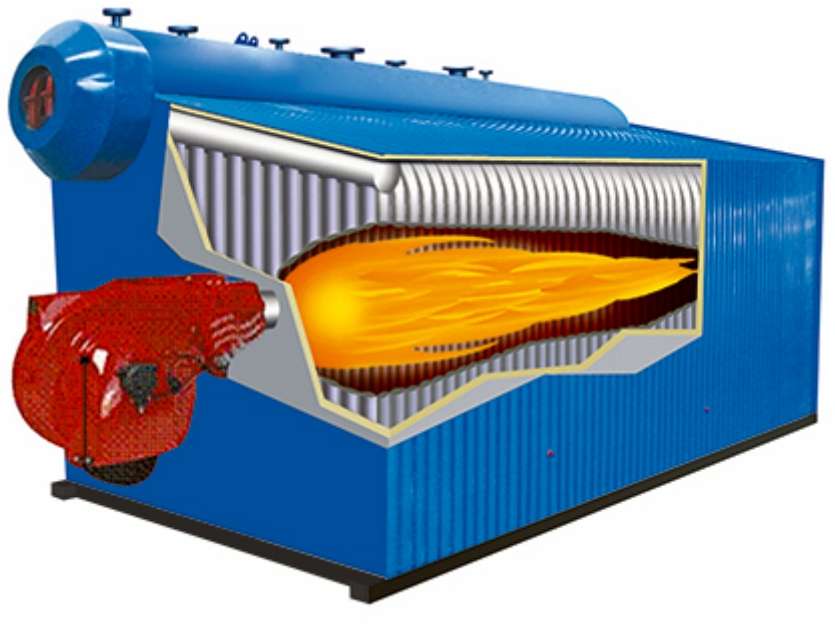
The working principle of oil and gas-fired boilers is relatively straightforward, yet it involves several key processes to efficiently convert fuel into heat. Here’s a breakdown of how these boilers operate:
1. Fuel Delivery
– For a gas-fired boiler, natural gas is supplied via a pipeline directly to the boiler. In the case of an oil-fired boiler, oil is pumped from a storage tank to the boiler.
2. Combustion
– The oil or gas fuel is mixed with air inside the burner. This mixture is then ignited by an electric igniter or pilot flame in the combustion chamber. The combustion process generates hot gases.
3. Heat Transfer
– The hot gases produced by the combustion process pass through a series of tubes or a heat exchanger. Water or another fluid circulates around these tubes or through the heat exchanger. The heat from the gases is transferred to the water, heating it up. This process effectively turns the water into hot water or steam, depending on the boiler’s purpose.
4. Circulation of Steam or Hot Water
– In the case of a steam boiler, the steam generated is circulated through pipes to radiators or to a process where heat is needed. The steam transfers its heat to the environment or process and condenses back into water. This water returns to the boiler to be reheated.
– In a hot water boiler, the heated water is circulated through a closed system where it releases its heat and is then returned to the boiler to be reheated.
5. Exhaust
– The combustion gases, after transferring their heat, are considered waste and need to be expelled. They are vented out of the boiler through a flue or chimney, thereby completing the combustion process.
Key Components Involved
– Burner: Mixes fuel with air and ignites it.
– Combustion Chamber: Where the fuel is burned to produce hot gases.
– Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the combustion gases to the water or steam.
– Pipes or Radiators: In a steam system, pipes carry steam to where heat is needed. In a hot water system, water circulates through radiators or a heating circuit.
– Controls: Including thermostats, pressure controls, and safety devices to regulate the boiler’s operation and ensure safety.
– Flue or Chimney: Expels combustion gases outside.
Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
Modern oil and gas-fired boilers are designed to achieve high levels of efficiency, often above 90%, meaning most of the energy in the fuel is converted into usable heat. They are also equipped with emission reduction technologies to minimize the environmental impact of the combustion process.
Oil & Gas fired Boiler
Ultimate Guide
2024

This guidebook serves as an extensive resource for professionals, engineers, and researchers interested in circulating fluidized bed Oil & Gas fired Boiler. It covers the fundamental principles, technology advancements, design considerations, operational challenges, and environmental impacts of Oil & Gas fired Boiler. Through detailed explanations, case studies, and practical insights, readers will gain a deep understanding of Oil & Gas fired Boiler technology and its applications in modern power and heat generation.














