Top Questions to Ask Industrial Biomass Boiler Suppliers Before Purchase
Purchasing an industrial biomass boiler is a strategic investment that involves complex decisions around fuel variability, emissions control, operational efficiency, and maintenance. A supplier’s ability to deliver a robust, customizable, and regulation-compliant solution directly affects your energy reliability and ROI. Asking the right technical and commercial questions is crucial to selecting a supplier who offers long-term performance and value—not just a boiler.
To evaluate potential industrial biomass boiler suppliers, ask questions about fuel compatibility, combustion technology, efficiency guarantees, emissions performance, ash handling, maintenance intervals, certifications (ASME, ISO, CE), automation, project references, and after-sales service. Clarify how the supplier adapts to diverse biomass fuels (wood chips, pellets, agricultural waste), handles moisture variations, and complies with local environmental regulations. This helps identify whether the supplier has real-world experience with complex biomass energy projects.
Here’s a list of critical questions to guide your supplier vetting process.
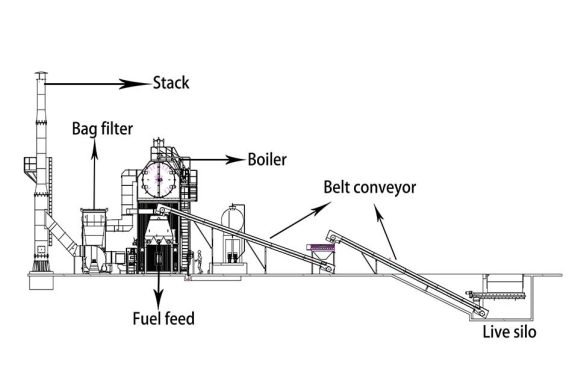
What Types of Biomass Fuel Can Your Boiler Handle, and How Do You Manage Varying Moisture Content?
Biomass fuels offer a renewable alternative to coal and oil, but they come with significant variability in composition, energy content, and moisture levels. These differences can drastically affect combustion stability, thermal efficiency, emissions, and even mechanical integrity if not properly managed. A high-performing biomass boiler must do more than simply “burn biomass”—it must be engineered for fuel diversity and equipped with systems to manage variable moisture content. Asking the right questions upfront ensures you invest in a solution that performs predictably and legally, even when fuel quality fluctuates.
Buyers must ask which biomass fuels (e.g., wood chips, rice husks, palm kernel shells, bagasse, RDF, sawdust, etc.) the boiler can handle efficiently, and how the system manages variations in moisture (from 15% to over 55%). This includes combustion chamber design, drying zones, air preheating, and feed rate modulation to maintain stable flame temperature and emissions control.
Without such adaptability, biomass boilers suffer from incomplete combustion, high CO emissions, slag buildup, and lower-than-promised efficiency—leading to higher O&M costs and regulatory challenges.
Biomass boiler systems must be explicitly designed to handle multiple biomass fuel types and manage their varying moisture content.True
Fuel variability affects combustion behavior, energy output, and emissions performance. Proper boiler design must address drying, feeding, and air control challenges.
Key Questions to Ask About Biomass Fuel Compatibility and Moisture Control
1. What Types of Biomass Fuel Has the Boiler Been Designed and Tested For?
| Biomass Fuel | Properties | Design Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Wood chips | GCV ~3,000–4,200 kcal/kg, 20–50% moisture | Requires drying zone or air preheater |
| Rice husk | Low bulk density, high silica | Needs special ash handling and erosion protection |
| Palm kernel shells | High CV (~4,300 kcal/kg), low ash | Efficient combustion but needs robust feeding |
| Bagasse | High moisture (40–55%) | Requires moisture control and steam drying options |
| Sawdust | Fine particle size, dry | Risk of uncontrolled combustion or blow-through |
| RDF/Biomass pellets | Engineered fuel | More stable but varies by supplier |
Ask:
Which fuels are compatible without major retrofit?
Do you have references with each of these fuels?
Can you share test reports with fuel GCV, moisture, and ash content?
2. What Is the Acceptable Moisture Range for Each Fuel?
| Fuel Type | Moisture Tolerance | Required Design Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Wood chips | 15–50% | Preheated primary air, larger combustion zone |
| Bagasse | 45–55% | Integrated drying conveyor, flue gas pre-dryer |
| Straw | 20–35% | Flame spreader, fluidized bed tolerance |
| RDF | 10–30% | Tuned air: fuel ratio and excess air control |
Ask:
What moisture levels were used during boiler design and CFD modeling?
Are fuel-specific efficiency penalties provided in the guarantee?
Does the feeding system include moisture sensors or metering adjustment?
3. What Combustion Technologies Are Used to Manage Fuel Variability?
| Combustion System | Moisture Management Ability |
|---|---|
| Grate furnace (step, reciprocating) | Handles coarse, high-moisture biomass with drying zone |
| Bubbling fluidized bed (BFB) | Tolerates mixed-size fuel with stable bed temperature |
| Circulating fluidized bed (CFB) | Best for multi-fuel, including RDF and high ash content |
| Suspension combustion | Requires low moisture and fine particles only |
Ask:
Which combustion system is recommended for our fuel portfolio?
How do you prevent clinker or slag buildup from incomplete drying?
What is the turndown ratio for partial load moisture variability?
4. How Is Moisture Controlled During Feeding and Combustion?
| Moisture Control Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Flue gas recirculation pre-dryer | Uses waste heat to pre-dry fuel |
| Steam tube fuel conveyor | Dries wet fuels like bagasse on the way to grate |
| Auto-adjustable grate speed | Matches feed rate with drying and burnout time |
| O₂ trim control | Adjusts air supply in real-time based on combustion feedback |
| Fuel moisture sensor | Real-time adjustment to combustion controls |
Ask:
Do you offer flue gas heat recovery for drying?
Is the feed system smart enough to self-tune based on moisture?
How is efficiency affected if moisture increases by 5–10%?
5. What Performance Guarantees Are Tied to Specific Biomass Fuels and Moisture Ranges?
| Guarantee Type | Typical Benchmark |
|---|---|
| Combustion Efficiency | ≥85–88% (with 25% moisture) |
| Thermal Efficiency | ≥80% (with ≤30% moisture biomass) |
| CO Emissions | <50 mg/Nm³ |
| Load Range | 30–100% of rated capacity |
| Moisture Limit Clause | ≤50% for full-load guarantee |
Ask for:
A detailed performance table by fuel and moisture level
Emissions guarantees under varied fuel mixes
Contractual LD clauses if efficiency drops under test conditions
Example: Biomass Boiler Running on Mixed Agricultural Waste
System: 35 TPH BFB boiler with mixed fuel feed
Fuels Used: 50% rice husk (20–22% moisture), 30% wood chips (40% moisture), 20% palm shells
Key Features:
Preheated air at 180°C for combustion
Cyclone + bag filter for PM < 15 mg/Nm³
Moisture sensor on conveyor for real-time grate speed control
| Performance | Measured Value |
|---|---|
| Thermal Efficiency | 85.2% (avg) |
| CO Emissions | 34 mg/Nm³ |
| SO₂ Emissions | 28 mg/Nm³ |
| Downtime Due to Slagging | <12 hours/year |
Summary
Biomass fuels offer clean energy—but only if your boiler is engineered for the real-world variability of fuel type and moisture. You must ask which fuels are compatible, how moisture is managed, and what happens when fuel conditions change. The right boiler supplier will offer flexible combustion technology, adaptive controls, and contract-backed performance guarantees tied to fuel quality. If the system can’t handle your fuel, it can’t meet your goals. Always ask for specifics, not assumptions—because in biomass, flexibility is performance.
What Is the Guaranteed Thermal Efficiency and Emissions Profile Under Full and Part Load?
When selecting an industrial biomass boiler, it’s not enough to evaluate nominal capacity or fuel compatibility alone. Thermal efficiency and emissions performance—especially across the full operating load range—are core to understanding the system’s operational cost, sustainability impact, and long-term compliance. Biomass combustion dynamics change significantly at part load due to fluctuating flame temperature, excess air levels, and fuel feed variability. Therefore, buyers must demand guaranteed thermal efficiency and emissions values for both full-load and part-load conditions. These values should be test-verified and contractually enforceable.
Buyers must request guaranteed thermal efficiency (typically ≥85–88%) and emissions performance (NOₓ, CO, PM) at both 100% rated load and turndown conditions (e.g., 60–70%). The boiler supplier should provide performance curves, test data, and emissions control strategy across the full load range, including during load swings and fuel variability.
Without clear guarantees, biomass boilers may burn inefficiently during off-peak hours, generating excess emissions and wasting fuel—undermining both environmental goals and profitability.
Thermal efficiency and emissions performance must be contractually guaranteed under full and part load conditions to ensure biomass boiler reliability and compliance.True
Boiler performance can decline sharply at partial load if not properly designed and tested. Guarantees protect fuel cost predictability and emissions permit integrity.
Key Questions to Ask About Efficiency and Emissions Guarantees
1. What Is the Guaranteed Thermal Efficiency at Full Load?
| Efficiency Metric | Typical Biomass Benchmark |
|---|---|
| Gross Efficiency (HHV) | ≥ 86–88% |
| Net Efficiency (LHV) | ≥ 83–85% |
| Fuel Moisture Basis | ≤ 30% (adjusted if >40%) |
Ask:
Is the efficiency based on Higher or Lower Heating Value (HHV or LHV)?
What is the guaranteed efficiency for each primary fuel type?
Is the performance verified via ASME PTC 4 or ISO 23145?
2. What Is the Efficiency and Emissions Profile at Part Load (e.g., 60–80%)?
| Load Level | Thermal Efficiency (Expected) | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| 100% Load | 86–88% | Optimal combustion and air control |
| 75% Load | 83–86% | Risk of excess air dilution |
| 60% Load | 80–84% | May require load-based tuning |
| 40–50% Load | 75–80% (if supported) | Risk of CO spike and instability |
Ask:
What is the guaranteed efficiency at each turndown point?
How is air-fuel ratio controlled at lower loads?
Are emissions guarantees still valid at 50–70% load?
3. What Are the Guaranteed Emissions Limits at Full and Part Load?
| Pollutant | Typical Target (mg/Nm³ @ 6% O₂) | Full vs Part Load Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| NOₓ | < 150 mg/Nm³ | May rise at high excess air or unstable flame |
| CO | < 50 mg/Nm³ | Often spikes at part load if combustion incomplete |
| PM (dust) | < 10–20 mg/Nm³ | Should remain stable with good filters |
| SO₂ | Fuel dependent | Typically negligible unless high-sulfur biomass |
| VOCs | < 20 mg/Nm³ | Controlled with proper flame temperature |
Ask:
Are these emissions limits constant across the full load range?
What test standards are used (ISO 8178, EN 13284, EPA Methods)?
Are these values guaranteed in writing or just indicative?
| Emissions Profile Sample – 12 TPH Biomass Boiler |
| Load (%) | Efficiency (%) | CO (mg/Nm³) | NOₓ (mg/Nm³) | PM (mg/Nm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 87.2 | 34 | 138 | 12 |
| 75% | 84.5 | 42 | 145 | 14 |
| 60% | 81.1 | 51 | 153 | 16 |
4. What Load Range Is Covered by These Guarantees?
| Turndown Ratio | Typical Range | What to Confirm |
|---|---|---|
| 3:1 or 4:1 | 30–100% load range | Stable flame, no shutdown cycling |
| 5:1 (advanced) | <25% load possible | May require special burner design |
Ask:
What is the stable minimum load without flame loss or CO peaking?
Is there auto-tuning or manual adjustment at part load?
Is a performance guarantee test conducted at both full and part loads?
5. How Are Efficiency and Emissions Monitored and Verified?
| Monitoring Tool | Function | Verification Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Emissions Monitoring System (CEMS) | Tracks CO, NOₓ, O₂ | EPA 40 CFR, EN 14181 |
| Flue gas analyzer | Efficiency audit | ASME PTC 4, ISO 8973 |
| DCS integration | Load-based air control | PID tuning curve for all loads |
| Heat balance software | Annual audit | Custom per plant process |
Ask:
Can I receive monthly or real-time performance dashboards?
Will emissions exceedances trigger automatic load reduction or alarm?
Are efficiency reports generated for compliance or savings tracking?
Summary Contract Clauses to Include
| Parameter | Guaranteed Value | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Efficiency @ 100% | ≥ 87.5% | 25% moisture wood chips |
| Efficiency @ 70% Load | ≥ 83% | Verified under PGT |
| CO @ all loads | ≤ 50 mg/Nm³ | Corrected to 6% O₂ |
| NOₓ @ all loads | ≤ 150 mg/Nm³ | With tuned air-fuel control |
| Turndown Ratio | At least 3:1 | No shutdown, stable emissions |
Summary
Thermal efficiency and emissions performance at both full and part load are the real indicators of a biomass boiler’s engineering quality and economic value. Don’t settle for single-point claims—demand load-specific guarantees, test data, and control logic that maintains performance across your full operational profile. Ask for contractual commitments, not theoretical ratings. Because in real-world biomass operation, consistency is the key to compliance, savings, and uptime.

How Is Ash Managed, and What Refractory or Cleaning Systems Are Used to Maintain Efficiency?
Biomass combustion generates a unique set of operational challenges—chief among them is ash management. Unlike fossil fuels, biomass often contains higher quantities of silica, potassium, and unburned organics, which can lead to slagging, fouling, corrosion, and efficiency loss if not addressed through smart design. That’s why prospective buyers must ask in detail how a biomass boiler supplier deals with ash removal, refractory wear, and in-situ cleaning to preserve long-term thermal performance and mechanical durability.
Buyers must ask how the boiler handles various types of biomass ash—fly ash, bottom ash, slag—and what refractory materials, cleaning systems, and anti-slagging mechanisms are used to maintain heat transfer and avoid fouling. These features directly affect fuel flexibility, emissions compliance, maintenance intervals, and overall efficiency.
If ash handling is under-designed or poorly managed, your boiler will suffer from unplanned downtime, increased pressure drop, high exit gas temperatures, and failed emissions tests.
Biomass boilers must include robust ash management and cleaning systems to maintain thermal efficiency and prevent slag buildup.True
Biomass ash contains corrosive and sintering elements that, if left unmanaged, reduce heat transfer and cause mechanical failure.
Key Questions to Ask About Ash Handling and Cleaning Systems
1. How Is Bottom Ash Collected and Discharged?
| Ash Type | Management Method | Recommended Features |
|---|---|---|
| Bottom Ash | Ash conveyors (wet/dry) | Enclosed system, refractory floor |
| Slag Clinker | Manual or auto rake-out | Ash cooling or slag crushers |
| Bed Ash (for FBC) | Bed drain or screw extruder | Supports high-ash, high-K fuels |
Ask:
Is bottom ash handled by dry mechanical screw or submerged scraper?
Can the system handle slag-forming fuels like rice husk or straw?
What is the ash discharge capacity in kg/hr?
2. What Is the Design Approach to Ash Fouling and Slag Prevention?
| Anti-Slagging Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| High-quality refractory with alkali resistance | Resists potassium and silica fusion |
| Soot blowers (air/steam) | Keeps tubes clean during operation |
| Bed temperature control (FBC) | Avoids ash melting point exceedance |
| Ash fusion modeling during design | Ensures tube spacing, heat flux optimization |
Ask:
What is the refractory material specification (e.g., high alumina, phosphate-bonded)?
Are critical areas (cyclones, superheaters) protected from ash impact erosion?
How often must ash be manually removed vs. auto-cleaned?
3. How Is Fly Ash Captured and Filtered From Flue Gas?
| Ash Removal System | Efficiency | Emissions Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Multicyclone Separator | 75–85% coarse PM | Pre-filter for ESP or baghouse |
| Bag Filter (Fabric Filter) | ≥ 99.5% of PM₂.₅+ | Keeps PM < 10–20 mg/Nm³ |
| ESP (Electrostatic Precipitator) | 95–99% | Low PM for wood/rice husk |
Ask:
What PM emissions guarantee do you provide?
How is filter cleaning managed—pulse jet, shaking, or reverse air?
Is fly ash recyclable or classified as hazardous?
4. What Cleaning Systems Are Included for Heat Transfer Surfaces?
| Cleaning System | Location | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic soot blowers | Superheater, economizer | Auto-controlled, every few hrs |
| Rapping devices | ESP and cyclone walls | Periodic via timer or sensor |
| Acoustic blowers | Convection zones | Low-noise option for fine ash |
| Manual access doors | Furnace, convection passes | 3–6 month manual cleaning cycle |
Ask:
Are cleaning systems automated or operator-activated?
Are high-fouling areas accessible for maintenance?
Can cleaning cycles be integrated into DCS for optimization?
5. What Is the Design Ash Content Range and Ash Handling Capacity?
| Fuel Type | Ash Content (%) | System Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Wood chips | 1–3% | Minimal buildup risk |
| Rice husk | 15–22% | High fouling, needs robust handling |
| Bagasse | 2–5% | Wet ash, often sticky |
| Corn stalk/straw | 5–12% | High potassium, clinker-prone |
Ask:
What is the design ash percentage supported (e.g., up to 25%)?
What ash load (kg/ton fuel) is used in system sizing?
Is the system proven on multiple high-ash fuels?
Real-World Case Example: Biomass Boiler With Ash Challenges
Fuel: Rice husk (18% ash), sawdust blend
Solution:
Fluidized bed combustion with bed ash removal screw
High-alumina refractory rated 1,400°C
6 pneumatic soot blowers (superheater/economizer)
Baghouse with automatic pulse jet cleaning (PM < 15 mg/Nm³)
72-hour ash hopper capacity, automated unloading
| Performance Result | Value |
|---|---|
| Downtime due to slag | < 2 days/year |
| Ash removal rate | ~170 kg/hr |
| Average PM emissions | 11.2 mg/Nm³ |
| Annual refractory maintenance | 1 intervention/year |
Summary
Ash management and fouling prevention aren’t afterthoughts in biomass boiler design—they are essential to maintaining combustion stability, heat transfer efficiency, and emissions compliance. You must demand clarity on ash discharge systems, refractory specs, soot blowing frequency, and filter performance. Ask about maintenance frequency and access for slag-prone fuels. If ash isn’t managed, your performance won’t last. And in biomass combustion, nothing clogs progress faster than unchecked clinker. Demand a clean burn—by design.

What Control Systems and Automation Options Are Available for Combustion and Feed Handling?
Unlike fossil fuels, biomass fuels vary widely in moisture, density, heating value, and combustion behavior, which introduces complex challenges in maintaining stable and efficient operation. Manual controls are not sufficient. To achieve consistent output, high efficiency, and regulatory emissions compliance, your biomass boiler must be equipped with intelligent, adaptive control systems. These systems must manage combustion air, fuel feed rate, flue gas recirculation, and ash handling in real time—especially as fuel properties and load demands shift. The right control and automation capabilities are what separate reliable, compliant biomass systems from those prone to trips, waste, and penalties.
Buyers must ask what combustion and fuel handling automation systems are offered, including PLC or DCS integration, oxygen trim control, adaptive feed rate tuning, remote monitoring, and emissions tracking. These systems should support real-time process feedback, predictive fault detection, and easy integration with existing plant SCADA.
A biomass boiler without smart control becomes a liability under variable fuel and load conditions. You’re not just buying steam—you’re buying stability through software and sensors.
Advanced control systems and combustion automation are essential for reliable, efficient, and compliant biomass boiler operation.True
Fuel variability and fluctuating demand require responsive, data-driven adjustment of feed rates, air distribution, and temperature zones to maintain performance and emissions targets.
Key Questions to Ask About Combustion and Feed Automation
1. What Type of Control System Is Provided—PLC, DCS, or Hybrid?
| System Type | Typical Use Case | Integration Capability |
|---|---|---|
| PLC-based (e.g., Siemens, Allen-Bradley) | Small to medium plants | Easy SCADA/DCS link |
| DCS (e.g., Emerson, Yokogawa, ABB) | Large-scale or multi-boiler setups | Integrated process control |
| Hybrid PLC + SCADA | Modular plants with digital oversight | Cloud/edge capable |
Ask:
What PLC/DCS brand and model is used?
Is the system open (Modbus, OPC-UA) or proprietary?
Can we integrate this into our plant-wide control room?
2. What Combustion Automation Features Are Included?
| Control Feature | Function | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| O₂ trim control | Adjusts excess air dynamically | Optimizes combustion, reduces CO |
| PID loop tuning | Manages pressure, temp, load | Stabilizes process during fuel variation |
| Grate speed control | Modulates combustion time | Adapts to fuel GCV and moisture |
| Flue gas recirculation (FGR) | Lowers NOₓ formation | Controlled based on load or temp |
Ask:
Is O₂ sensor feedback closed-loop or manual?
Can air-fuel ratio be tuned per fuel batch?
How is flame instability detected and resolved?
3. How Is Biomass Fuel Feeding Controlled and Adjusted?
| Feeding Component | Automation Feature | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Screw conveyors / drag chains | VFD-based speed control | Matches load and moisture shift |
| Rotary feeders | Sensor-triggered pulse control | Avoids fuel surges and bridging |
| Load cells / flow meters | Mass flow feedback | Improves feed precision |
| Moisture sensors | Adjusts feed rate + air | Compensates for wet/dry shifts |
Ask:
Are multiple feed points controlled individually or centrally?
Can we automate feed distribution based on fuel mix?
Is blockage detection built in (torque or limit sensors)?
4. What Real-Time Monitoring and Remote Access Options Are Available?
| Monitoring Function | Data Tracked | Platform |
|---|---|---|
| HMI/SCADA dashboard | Temp, pressure, emissions, feed rate | Touchscreen + remote desktop |
| Remote diagnostics | Fault alerts, performance curves | Web/cloud enabled |
| Historical trend analysis | Fuel use, efficiency, emissions | CSV/SQL data logs |
| Predictive maintenance | Vibration, wear, sensor alerts | AI-assisted if enabled |
Ask:
Can we monitor remotely via PC or mobile?
Is alarm escalation included (email/SMS)?
Is diagnostic data accessible for third-party audit?
5. How Are Emissions Controlled and Recorded Automatically?
| Emission Control | Linked Sensor/Actuator | Automation Level |
|---|---|---|
| NOₓ control | Burner staging, FGR, SNCR | Auto-valve and injection control |
| CO control | O₂ trim, fuel-air ratio | PID-linked loop |
| PM control | Baghouse pulse jet frequency | Pressure drop sensors |
| SO₂ control (if needed) | Sorbent injection | Lime dosing pump automation |
Ask:
Is CEMS data integrated into control logic?
Are emissions logged and formatted for regulatory upload?
Can tuning routines be automated based on NOₓ/CO targets?
Example Automation Setup – 20 TPH Biomass Boiler
System Overview:
Siemens S7-1500 PLC with integrated 10” touchscreen HMI
Feed rate and combustion air auto-tuned by real-time O₂ sensor
Moisture-adjusted fuel load modulation via infeed screw
CEMS-linked emissions correction logic
Baghouse filter cleaning cycle based on ΔP feedback
| Parameter | Real-Time Control | Target Range |
|---|---|---|
| Bed temperature | PID-controlled via fuel feed | 820–880°C |
| O₂ in flue gas | O₂ trim via VFD dampers | 4.0–6.0% |
| CO emissions | Combustion feedback loop | <45 mg/Nm³ |
| Fuel feed rate | Moisture-sensor adjusted | ±5% accuracy |
Summary
Biomass boilers require more than good combustion—they demand smart combustion. Only a system with robust automation and real-time control can adapt to the unpredictable nature of biomass fuel and still deliver efficient, stable, and compliant performance. From PID loops to emissions tuning, every control element adds operational value. Ask for proof of automation—screen layouts, sensor specs, and integration maps. Because in biomass operations, control isn’t a convenience—it’s a competitive edge.

What Certifications, Compliance Standards, and Quality Controls Do You Meet?
The credibility and performance of a biomass boiler supplier are anchored in one fundamental principle: compliance with internationally recognized design, safety, environmental, and quality standards. Without certifications like ASME, ISO, and CE, or without a traceable quality assurance system, you risk buying equipment that may fail inspections, void insurance requirements, or operate unreliably under regulatory scrutiny. Certifications are not mere badges—they are proof that the supplier designs, fabricates, tests, and delivers to standards that protect your investment and ensure long-term operation.
Buyers must ask which certifications the biomass boiler system meets—such as ASME Section I (pressure vessels), CE PED (Pressure Equipment Directive), ISO 9001/14001/45001 for management systems—and what quality assurance/quality control procedures are embedded in manufacturing. These standards are essential for safety, emissions compliance, and installation approvals.
If the boiler isn’t certified, it may not even be legally installed or operated in your country. And if the supplier can’t prove quality control, you inherit the risk.
Biomass boiler suppliers must hold relevant design, safety, and quality management certifications to ensure regulatory compliance and long-term reliability.True
Certifications like ASME, CE, and ISO validate pressure safety, fabrication consistency, emissions compliance, and operational durability under global and local standards.
Key Questions to Ask About Certification and Quality Control
1. What Pressure Equipment Certifications Do You Hold?
| Certification | Scope | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| ASME Section I (“S” Stamp) | Power boilers | Globally recognized pressure safety |
| ASME Section VIII (“U” Stamp) | Pressure vessels | Economizers, preheaters, drums |
| CE Marking (PED 2014/68/EU) | EU Pressure Equipment Directive | Legal entry into EU markets |
| EN 12952 / EN 12953 | Shell and water-tube boilers (Europe) | Compliance for EU installations |
Ask:
Is the final boiler stamped and accompanied by an ASME or CE nameplate?
What notified body oversees your CE or PED process (e.g., TÜV, SGS)?
Can I see a sample Certificate of Conformity?
2. What ISO Management Systems Are in Place?
| ISO Standard | Function | Why It’s Critical |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management | Ensures design and production repeatability |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Emissions-conscious fabrication process |
| ISO 45001 | Occupational Health & Safety | Safe production, assembly, and commissioning |
| ISO 50001 (optional) | Energy Management | Efficient system lifecycle support |
Ask:
Are these certifications current and third-party audited?
Do you apply ISO 9001 principles to subcontractors?
Can you provide sample internal audit results?
3. What Local or Regional Standards Do You Meet?
| Region | Relevant Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| India | Indian Boiler Regulations (IBR) | Mandatory for pressure equipment |
| China | GB 150, GB 13223 (ULE) | National boiler and emissions standards |
| Russia / EAEU | TR CU 032 / GOST | Regional pressure and safety regulations |
| North America | UL/CSA (electrical) | Panel and wiring compliance |
| Middle East | SASO / GSO / IEC integration | Local pressure and emissions codes |
Ask:
Have you delivered projects in our regulatory region?
Do you have field inspectors or liaison teams for local approvals?
Can you register the boiler with national authorities pre-delivery?
4. What Quality Control Procedures Are Used During Fabrication?
| QC Activity | Purpose | Expected Proof |
|---|---|---|
| Material Traceability | Ensures steel grade and origin match specs | Material Test Reports (MTRs) |
| Welding Inspection | Prevents cracking and porosity | Radiography, UT, PT with signed logbooks |
| Dimensional Checks | Confirms drawing tolerances | Alignment and fit-up reports |
| Hydrostatic Testing | Verifies pressure vessel integrity | Pressure logs with third-party witness |
| Paint/Coating QC | Prevents corrosion and chemical failure | DFT readings, surface prep grades |
Ask:
Do you issue ITP (Inspection Test Plan) or QCP (Quality Control Plan)?
Can we participate in Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT)?
Is third-party inspection supported?
5. Do You Provide Documentation for QA Traceability and Audits?
| Document Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Data Book / Dossier | Legal and technical audit |
| Weld maps and WPS | Fabrication record and warranty protection |
| Calibration certificates (sensors, gauges) | Measurement assurance |
| FAT reports | Operational verification before shipment |
Ask:
Do you deliver a digital and hard copy QA dossier with the boiler?
Is document delivery tied to payment milestones?
Are emission system components (CEMS, baghouse) certified?
Case Study: ISO and CE-Certified 15 TPH Biomass Boiler
Standards Applied:
CE PED H1 Module with TÜV Nord inspection
ISO 9001 for full fabrication and delivery traceability
ASME “S” stamp for superheater modules
EN 12952 water-tube boiler framework
QA/QC Documentation Delivered:
Full weld map with WPS, PQR, WQR
Radiography reports with traceable locations
Hydrotest certificate (210 bar for 150 bar design)
Painting system per ISO 12944 C4
| Result | Impact |
|---|---|
| 100% regulatory acceptance | No delays during commissioning |
| 92% QA score in 3rd-party audit | Top-tier vendor classification |
| 0 NCRs during FAT and delivery | Seamless documentation handover |
Summary
Certifications and quality control are the foundation of a safe, compliant, and high-performance biomass boiler. Don’t rely on verbal assurances—ask for stamped plates, signed test records, and third-party audit reports. Only a supplier that meets ASME, CE, ISO, and local regulatory standards can deliver a boiler that performs reliably, passes inspection, and minimizes lifecycle risk. Choose a partner who fabricates with documentation as carefully as they weld with steel—because paper, like pressure, must hold.

What References, Performance Guarantees, and Post-Sale Support Services Do You Provide?
For industrial biomass boiler buyers, the difference between a successful long-term investment and an operational liability often hinges on one thing: supplier credibility. That credibility is built on three pillars—project references, contractual performance guarantees, and comprehensive post-sale support. A supplier with a proven track record across various fuels and industries, measurable guarantee-backed performance, and committed service capability is far more likely to deliver lasting value than one that merely meets specifications on paper.
Buyers must ask for specific project references (with fuel types, capacities, locations), contractual performance guarantees (thermal efficiency, emissions, steam output), and detailed post-sale service offerings (technical support, spare parts, remote diagnostics, and maintenance contracts). These elements are essential to verifying real-world competence and ensuring long-term plant reliability.
Don’t accept vague promises—request documented proof and real commitments. In biomass systems, experience and accountability matter more than marketing.
Performance guarantees, client references, and post-sale support are key indicators of a biomass boiler supplier’s reliability and long-term value delivery.True
They demonstrate real-world performance, legal commitment to results, and ongoing support infrastructure for safe and efficient operations.
Key Questions to Ask About Experience, Guarantees, and Support
1. Can You Provide Project References for Similar Biomass Boiler Installations?
| Reference Detail | What to Request |
|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Match your target biomass (wood chips, rice husk, etc.) |
| Capacity | Match or exceed your required TPH and pressure |
| Location | Similar regulatory or climatic region preferred |
| Application | Industrial steam, power generation, CHP, drying |
Ask:
Can you share reference letters or contact info?
What were the load conditions and emissions achieved?
Were there any change orders or performance deviations?
2. What Performance Guarantees Do You Offer, and How Are They Enforced?
| Guaranteed Parameter | Typical Benchmark | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Efficiency | ≥ 85–88% (HHV) | ASME PTC 4 or ISO 23145 |
| Steam Output | Rated ±2% | 24–72h PGT trial |
| Emissions | NOₓ <150 mg/Nm³, PM <20 mg/Nm³, CO <50 mg/Nm³ | EN 13284, ISO 8178 |
| Load Range | 30–100% stable turndown | Witnessed startup to max load |
| Moisture Tolerance | Up to 45% (fuel-dependent) | Verified by feed and O₂ tuning system |
Ask:
Are guarantees backed by LD (liquidated damages) clauses?
What are the test conditions (fuel GCV, pressure, moisture)?
What corrective action is taken if results fall short?
| Sample Performance Guarantee Table |
| Parameter | Guaranteed Value | Test Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Efficiency | ≥ 87.5% | Wood chips, 30% moisture |
| Steam Output | 15 TPH ±2% | 10 bar, saturated |
| NOₓ | < 140 mg/Nm³ | Corrected to 6% O₂ |
| CO | < 40 mg/Nm³ | Full and 75% load |
| Downtime/year | < 1.5% | Tracked via remote SCADA |
3. What Post-Sale Services Do You Offer After Commissioning?
| Service Type | Details | Best Practice Expectation |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Support | Hotline, remote diagnostics, on-site visits | 24/7 availability with SLA response times |
| Spare Parts Supply | Stocking, logistics, warranty coverage | Local warehouse or 2–3 week delivery commitment |
| Operator Training | Startup and refresher training | Certified, site-specific sessions |
| Preventive Maintenance | Mechanical and combustion inspections | Quarterly/biannual visits |
| CEMS & Compliance Support | Emissions calibration and tuning | Annual or by regulation cycle |
Ask:
Do you offer long-term service agreements (LTSAs)?
What spare parts are included in startup and annual kits?
Is remote tuning or real-time monitoring included in the package?
4. Do You Provide Remote Diagnostics, Trend Analysis, and Emissions Monitoring?
| Digital Feature | Function | Platform |
|---|---|---|
| SCADA/DCS integration | Real-time parameter control | Local HMI or plant network |
| Remote monitoring portal | Access to boiler health metrics | Web-based or mobile app |
| Emissions data logging | Stores NOₓ, CO, PM data | CEMS or stack sensor feed |
| Predictive maintenance alerts | Detects fan wear, fouling, drift | AI-based if available |
Ask:
What is included in your digital support suite?
Are cloud dashboards or alerts mobile-accessible?
Can data be exported for audits and performance tracking?
5. What Support Is Provided During and After Commissioning?
| Commissioning Phase | Supplier Role |
|---|---|
| Cold commissioning | Mechanical/electrical checks |
| Hot commissioning | Burner startup, tuning, steam blow |
| Performance Testing | Verifies guarantees over 24–72 hrs |
| Handover & Training | Full operator walkthrough |
| Post-handover support | 30–90 days on-call support or embedded tech |
Ask:
Will engineers be deployed on-site during commissioning?
Is FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) included and witnessed?
What documentation is provided for O&M and emissions logs?
Case Example: Verified 18 TPH Biomass Boiler – Mixed Fuel CHP
Client: Agro-industrial cogeneration plant
Fuel: 60% wood chips (35% moisture), 40% rice husk (18% ash)
Supplier Support:
5-year LTSA with quarterly inspections
Cloud-based emissions monitoring and trend dashboard
Remote burner tuning via VPN
Spare parts warehouse within 300 km
CEMS calibration and audit prep included
| Guaranteed | Measured |
|---|---|
| Efficiency ≥ 86% | Achieved 87.3% |
| NOₓ < 150 mg/Nm³ | 134 mg/Nm³ |
| CO < 50 mg/Nm³ | 31 mg/Nm³ |
| Steam Output ≥ 18 TPH | 18.2 TPH average |
Summary
References, performance guarantees, and post-sale support are the litmus test of a biomass boiler supplier’s real-world competence. Ask for documented results, not promises. Demand signed guarantees, not theoretical values. Insist on detailed service plans, not vague support claims. Because once the boiler is fired, it’s these three elements—experience, commitment, and service—that keep it burning clean, efficient, and compliant for years to come. In biomass, your best protection is proof.
🔍 Conclusion
Choosing the right biomass boiler supplier means choosing a partner who understands your fuel, your industry, and your regulatory environment. By asking these targeted questions, you can avoid costly mismatches and ensure your boiler system delivers clean, reliable, and cost-effective energy for years to come.
📞 Contact Us
💡 Need help evaluating biomass boiler suppliers? We offer technical vetting, bid comparison, and performance assessments to support your procurement process.
🔹 Let us help you choose a biomass boiler supplier who delivers on fuel flexibility, compliance, and long-term value. 🌱🔥✅
FAQ
What certifications and standards do your biomass boilers meet?
Ensure the supplier complies with:
ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code
ISO 9001 / 14001 quality and environmental standards
CE marking for international compliance
Biomass sustainability standards (e.g., ENplus, BSL, FSC-certified fuels)
These ensure reliability, safety, and eligibility for incentives or carbon credits.
What biomass fuels are compatible with your boilers?
Ask about supported fuel types, such as:
Wood chips, wood pellets, and sawdust
Agricultural waste (e.g., rice husks, corn cobs, bagasse)
RDF (Refuse-Derived Fuel) and MSW (Municipal Solid Waste)
Also verify moisture content tolerance, ash content limits, and fuel preparation requirements.
What are the thermal efficiency and emissions levels of your systems?
Request:
Certified thermal efficiency ratings (typically 80–90%)
Emission data on NOx, SOx, PM, and CO
Compliance with local and international emissions regulations
Options for emission controls like cyclones, baghouses, or scrubbers
What automation and monitoring systems are included?
Ask about:
Fuel feeding automation and ash removal
Real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, or SCADA integration
Alarm and shutdown interlocks for pressure, temperature, and feed consistency
Smart control systems to optimize combustion and reduce manual operation
What after-sales services and support do you provide?
Key services to confirm include:
Installation and commissioning
Operator training
Scheduled maintenance programs
Spare parts supply for at least 10 years
On-site or remote technical support
References
ASME Boiler Manufacturing Certification – https://www.asme.org
ISO Certification Database for Manufacturers – https://www.iso.org
Biomass Fuel Standards and Sustainability Labels – https://www.enplus-pellets.eu
Boiler Emissions Compliance – EPA Guidelines – https://www.epa.gov
Biomass Boiler Efficiency and Fuel Flexibility Reports – https://www.iea.org
Smart Boiler Automation Systems – https://www.automation.com
Boiler Operation & Maintenance Best Practices – https://www.sciencedirect.com
Energy Performance Benchmarking – DOE – https://www.energy.gov
Case Studies of Biomass Boiler Installations – https://www.researchgate.net
Biomass Emissions Control Technologies – https://www.bioenergyconsult.com

