When planning an industrial or commercial heating system, many operators struggle with whether to select a steam boiler or a hot water boiler. Choosing the wrong type can lead to inefficiency, safety risks, and higher operational costs, since the two systems are designed for different applications and performance requirements.
The key difference between steam boilers and hot water boilers is the operating medium and pressure: steam boilers generate pressurized steam for power generation, sterilization, and process heating, while hot water boilers produce heated water (typically below 100–120°C) for building heating, domestic hot water, or low-temperature processes. Steam boilers operate at higher pressures and temperatures, requiring more robust safety systems, whereas hot water boilers are generally simpler, safer, and more cost-effective for moderate heating needs.
Understanding these differences ensures companies select the right boiler for efficiency, safety, and long-term performance.

How Does the Operating Principle Differ Between Steam Boilers and Hot Water Boilers?
Steam boilers and hot water boilers may look similar, but their operating principles and applications are quite different. Understanding the distinction is critical when choosing the right system for an industrial process or facility.
In short: Steam boilers generate and distribute steam for heating and process use, while hot water boilers heat and circulate pressurized water for space or process heating.
🔹 Operating Principle Comparison
| Feature | Steam Boiler | Hot Water Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Working Medium | Produces steam (saturated or superheated) | Heats and circulates hot water |
| Heat Transfer | Converts feedwater into steam via boiling | Raises water temperature without phase change |
| Operating Pressure | Medium to high pressure (e.g., 6 bar – 100+ bar) | Usually low to medium pressure (< 30 bar) |
| Distribution System | Steam piping with condensate return | Closed loop piping with pumps |
| Applications | Power generation, chemical processes, food industry, sterilization | Building heating, district heating, low-temp industrial processes |
🔹 Why It Matters
Steam boilers are chosen where high heat transfer, sterilization, or power generation is needed.
Hot water boilers are preferred where stable, controlled heating is required at lower pressures.
Choosing incorrectly can lead to overdesign, higher costs, or safety issues.
✅ Bottom line:
The main difference lies in phase change — steam boilers convert water to steam for high-energy processes, while hot water boilers only heat water for circulation. Selecting the right type ensures efficiency, safety, and long-term reliability.

What Are the Typical Temperature and Pressure Ranges for Each Type of Boiler?
One of the most important distinctions between steam boilers and hot water boilers is the temperature and pressure they operate under. These ranges determine their suitability for different industrial and heating applications.
In short: Steam boilers operate at higher pressures and temperatures to generate usable steam, while hot water boilers run at lower pressures and moderate temperatures for heating purposes.
🔹 Typical Operating Ranges
| Boiler Type | Temperature Range | Pressure Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Pressure Steam Boiler | ~100°C to 165°C (212°F to 330°F) | Up to 15 psi (1 bar) | Laundry, food processing, small plants |
| High-Pressure Steam Boiler | 165°C to 565°C (330°F to 1050°F, for superheated steam) | 16 bar to 200+ bar (230 psi to 3000 psi) | Power plants, refineries, chemical industries |
| Hot Water Boiler (Standard) | 60°C to 120°C (140°F to 250°F) | < 6 bar (90 psi) | Building heating, district heating |
| High-Temperature Hot Water (HTHW) Boiler | 120°C to 250°C (250°F to 480°F) | 6 bar to 25 bar (90 psi to 360 psi) | Industrial heating networks, large facilities |
🔹 Why These Ranges Matter
Safety → Steam requires strong pressure vessels and stricter safety controls.
Efficiency → High-pressure steam transfers energy quickly for industrial processes.
Application fit → Hot water systems are safer and simpler for comfort heating.
✅ Bottom line:
Steam boilers: higher temperature and pressure, suited for power and process industries.
Hot water boilers: lower ranges, ideal for building and industrial heating.
Choosing the right boiler depends on required output, safety considerations, and application demands.
In Which Industrial and Commercial Applications Are Steam Boilers Preferred?
Steam boilers are the backbone of industries that need high heat energy, sterilization, or power generation. Unlike hot water boilers, which only transfer sensible heat, steam boilers provide latent heat, making them far more effective for processes that require rapid, intense energy transfer.
In short: Steam boilers are preferred in industries where high-pressure steam is essential for production, sterilization, or mechanical power.
🔹 Typical Applications of Steam Boilers
| Sector | Application | Why Steam Is Preferred |
|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Steam turbines in power plants | High-pressure steam drives turbines to produce electricity efficiently |
| Food & Beverage | Brewing, sterilization, cooking, pasteurization | Steam provides clean, controllable, and uniform heating |
| Textile Industry | Dyeing, drying, pressing | Steam offers consistent heat for fabric treatment |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization, reactor heating | Pure steam ensures hygienic and controlled processing |
| Chemical & Petrochemical | Distillation, cracking, refining | High-pressure steam is essential for chemical reactions and heat transfer |
| Pulp & Paper | Pulp digesters, drying machines | Steam supplies the large thermal energy needed for paper production |
| Hospitals & Healthcare | Sterilizers, laundry, humidification | Steam provides sanitary, reliable heating |
| Manufacturing | Rubber curing, metal finishing, process heating | Steam delivers uniform, high-energy heat |
🔹 Why Steam Wins Over Hot Water
Higher energy transfer capacity due to latent heat of vaporization.
Flexibility — can power turbines or provide direct heating.
Sterility — clean steam is essential in food and pharma.
Scalability — from small industrial boilers to large utility-scale power plants.
✅ Bottom line:
Steam boilers are chosen wherever high-pressure, high-energy heat transfer is required — from power plants to food factories. Their ability to deliver consistent, controllable steam makes them indispensable in many critical industries.
When Are Hot Water Boilers the Better and More Economical Choice?
While steam boilers dominate in heavy industries, hot water boilers are often the smarter and more cost-effective choice for heating-focused applications. They operate at lower pressures and temperatures, which makes them safer, easier to maintain, and more economical for many commercial and light industrial uses.
In short: Hot water boilers are preferred when the goal is efficient space heating, hot water supply, or moderate process heating without the complexity and costs of steam systems.
🔹 Typical Applications of Hot Water Boilers
| Sector | Application | Why Hot Water Boilers Fit Best |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Buildings | Hotels, offices, schools, hospitals | Provides reliable heating and domestic hot water at lower cost |
| District Heating | Urban residential or mixed-use areas | Hot water distribution is more efficient and safer than steam for long piping runs |
| Light Industry | Food processing (wash water, cleaning), beverage plants | Adequate for processes that don’t require high-pressure steam |
| Greenhouses & Agriculture | Soil heating, greenhouse heating | Hot water provides controlled and uniform temperatures |
| Manufacturing Support | Space heating for workshops, warehouses | Lower operating cost compared to steam |
| Institutional Facilities | Universities, military bases, correctional facilities | Centralized heating with simpler operation and reduced risk |
🔹 Why Hot Water Boilers Are More Economical
Lower operating pressure → reduces safety risks and inspection requirements.
Higher efficiency → minimal energy wasted as latent heat, since no phase change occurs.
Lower installation cost → simpler piping and fewer safety devices needed.
Reduced maintenance → no condensate return system required.
Ease of operation → simpler controls, ideal where steam isn’t essential.
✅ Bottom line:
Hot water boilers are the better and more economical choice when heating or moderate-temperature processes are the priority. They save on equipment, fuel, and maintenance while providing reliable, safe operation for commercial and institutional users.
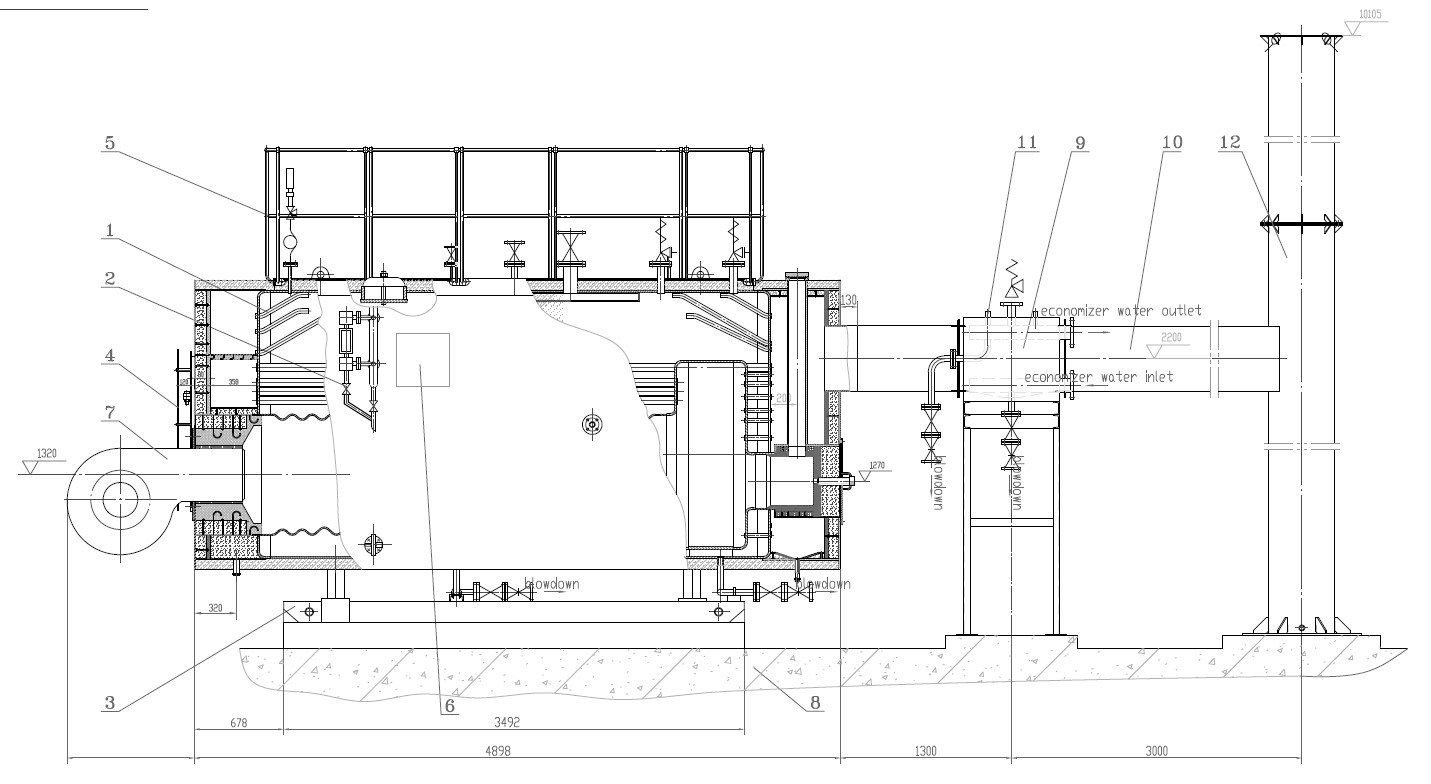
How Do Safety Systems and Regulations Differ Between the Two Boiler Types?
Steam and hot water boilers may look similar, but the safety systems and regulatory requirements are not the same. Because steam boilers operate at higher pressures and temperatures, they face stricter codes, more protective devices, and tighter inspection schedules compared to hot water boilers.
In short: Steam boilers require more safety controls and regulatory oversight due to the risks of high-pressure steam, while hot water boilers operate under simpler safety frameworks.
🔹 Safety Systems: Steam vs. Hot Water
| Aspect | Steam Boiler | Hot Water Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Risk | High-pressure steam release (explosion hazard) | Lower risk, mainly leaks or overheating |
| Key Safety Devices | Safety relief valves, low-water cutoff, flame safeguard, pressure controls, high-limit cutouts, automatic blowdown | Relief valves, temperature & pressure (T&P) controls, low-water protection |
| Water Level Control | Critical – must avoid low-water conditions | Less critical – system is always water-filled |
| Combustion Safeguards | Mandatory flame detection, burner interlocks, purge sequences | Required, but less complex in design |
| Shutdown Protocols | Automatic interlocks for high pressure, flame failure, low water, high temperature | High temperature or overpressure shutdowns |
🔹 Regulations and Inspections
Steam Boilers:
Governed by ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (Section I or IV) and national boiler safety codes.
Often require annual or biannual internal inspections by certified inspectors.
Operators may need licensing or certification.
Must have documented logbooks, water chemistry records, and safety test results.
Hot Water Boilers:
Typically fall under lower-pressure ASME Section IV standards.
Inspection frequency is lighter; in some regions, small hot water boilers may not require external inspection.
Operator licensing is often not mandatory.
Safety focus is mainly on relief valves and T&P controls.
🔹 Why It Matters
Steam boilers → higher risk = stricter compliance, more safety equipment, and higher operational oversight.
Hot water boilers → simpler systems, lower regulatory burden, easier for facilities with limited staff.
✅ Bottom line:
Steam boilers demand robust safety systems and strict regulatory compliance, while hot water boilers operate under simpler, lower-pressure frameworks. The difference in oversight reflects the much higher risk profile of steam.

What Are the Installation, Maintenance, and Operating Cost Differences Between Steam and Hot Water Boilers?
When choosing between steam boilers and hot water boilers, cost is often the deciding factor. While both provide heating energy, their installation complexity, maintenance needs, and long-term operating costs differ significantly due to the higher pressure and safety requirements of steam systems.
In short: Steam boilers cost more to install and maintain, but they are essential for high-energy industrial processes. Hot water boilers are more economical for heating and moderate-temperature applications.
🔹 Cost Comparison Overview
| Cost Category | Steam Boiler | Hot Water Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Higher cost due to pressure-rated vessels, steam piping, condensate return, and stricter code compliance | Lower cost with simpler piping, pumps, and controls |
| Maintenance | Frequent inspections, water chemistry management, blowdown, tube cleaning, safety valve testing | Lower frequency of inspections, fewer chemical treatments, simpler upkeep |
| Operating Costs | Higher fuel consumption (phase change requires latent heat), additional losses in condensate return | More efficient for heating-only needs (no latent heat losses) |
| Operator Requirement | Licensed operator often required for steam systems | Often can run with general facility staff |
| Regulatory Compliance | Annual/biannual inspections and documentation required | Minimal inspections in many jurisdictions |
| Lifecycle Costs | Higher due to energy and maintenance demands | Lower overall lifecycle costs, especially for heating applications |
🔹 Why These Differences Exist
Steam boilers require more robust construction and controls to handle high pressures, which increases installation cost.
Water chemistry management is more critical for steam systems to prevent scaling, corrosion, and carryover.
Hot water boilers avoid condensate return systems and operate at lower pressures, reducing both complexity and expense.
✅ Bottom line:
Choose a steam boiler if your process demands high-pressure steam for power, sterilization, or chemical reactions.
Choose a hot water boiler if your application is primarily heating or moderate process temperatures — it will be far more economical to install and run.
🔍 Conclusion
Steam boilers and hot water boilers serve different purposes: steam systems are ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature industrial processes, while hot water boilers are more suitable for low-to-medium temperature heating and hot water supply. Selecting the right option ensures operational reliability, cost savings, and compliance.
📞 Contact Us
💡 Unsure whether you need a steam or hot water boiler? We provide engineering consultation, boiler system design, and turnkey solutions tailored to your exact heating or process requirements.
🔹 Contact us today to choose the right boiler system for your project. ♨️🏭✅
FAQ
What is the main difference between steam boilers and hot water boilers?
The primary difference lies in the output:
Steam boilers produce steam at various pressures for industrial processes, power generation, or heating.
Hot water boilers heat and circulate hot water for space heating or low-temperature industrial applications.
Steam systems operate at higher pressures and temperatures, while hot water systems are typically lower-pressure and safer.
Which industries use steam boilers vs. hot water boilers?
Steam boilers are used in power plants, chemical plants, refineries, textile mills, and food processing, where high-temperature steam is needed.
Hot water boilers are used in residential heating, commercial buildings, schools, and hospitals for heating water or supplying district heating.
Are steam boilers more efficient than hot water boilers?
Hot water boilers are generally more efficient for space heating, as there is less energy loss compared to steam transport.
Steam boilers can be less efficient due to condensate return losses and heat transfer inefficiencies, but they are essential when high-temperature steam is required.
What are the installation and maintenance differences?
Steam boilers require heavier piping, blowdown systems, condensate recovery, and strict water chemistry control.
Hot water boilers are simpler, requiring fewer components, lower maintenance, and reduced operational risk.
Which boiler is more cost-effective in the long term?
For industrial applications requiring high-pressure steam, steam boilers are necessary despite higher costs.
For heating and hot water supply, hot water boilers are more cost-effective, energy-efficient, and easier to maintain.
References
U.S. Department of Energy – Boiler Basics – https://www.energy.gov
ASME Boiler Standards – Steam vs Hot Water Systems – https://www.asme.org
Spirax Sarco – Types of Boilers – https://www.spiraxsarco.com
Forbes Marshall – Boiler Efficiency Comparison – https://www.forbesmarshall.com
Cleaver-Brooks – Hot Water vs Steam Boilers – https://www.cleaverbrooks.com
Babcock & Wilcox – Boiler Applications – https://www.babcock.com
Engineering Toolbox – Steam vs Hot Water Properties – https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com
IEA – Industrial Boiler Use – https://www.iea.org
ResearchGate – Boiler Efficiency Studies – https://www.researchgate.net
EnergyStar – Commercial Boiler Systems – https://www.energystar.gov

