Industrial Steam Boiler Choices: Fire-Tube vs. Water-Tube Explained
Industrial Steam Boiler Choices: Fire-Tube vs. Water-Tube Explained
Choosing the best Industrial Steam Boiler is very important for many businesses. Every place must answer a big question: What makes fire-tube and water-tube boilers different? Picking the right one changes how well a plant works, how much money it uses, and how safe it is. Each design has special benefits for certain jobs.
Key Takeaways
Fire-tube boilers have hot gases inside tubes. Water surrounds these tubes. They are simple and easy to use. They work best for small or medium steam needs.
Water-tube boilers have water inside tubes. Hot gases are around the tubes. These boilers can handle higher pressure. They work more efficiently. They are safer for big or high-pressure jobs.
Water-tube boilers save fuel and energy over time. They cost more at first. Fire-tube boilers cost less at the start. But they use more fuel. They also take longer to start.
Regular maintenance is important. This includes weekly checks and yearly inspections. It keeps boilers safe and efficient. It also makes them reliable. Maintenance helps stop breakdowns and lowers repair costs.
Picking the right boiler depends on many things. You need to think about steam pressure and capacity. Space, budget, and what you need also matter. Experts can help you choose the best boiler for your facility’s goals.
Key Differences
Design
Fire-tube and water-tube boilers are built in different ways. In a fire-tube boiler, hot gases go through tubes inside a big tank of water. The heat from the gases makes the water turn into steam. Water-tube boilers work in the opposite way. Water moves inside the tubes, and hot gases flow around them. This design helps water-tube boilers handle higher pressure and heat. The table below shows some main design differences:
Feature | Fire-Tube Boiler | Water-Tube Boiler |
|---|---|---|
Water Location | Around tubes in the shell | Inside the tubes |
Hot Gas Location | Inside tubes | Around tubes |
Water Volume | Large | Small |
Pressure Capability | Lower | Higher |
Footprint | Larger | Smaller |
Note: Water-tube boilers use about 10% as much water as fire-tube boilers. This makes them safer and faster to start.
Operation
How each boiler works changes how it fits in a system. Fire-tube boilers run at lower pressures, between 10 and 25 bar. They can start in 15 to 30 minutes. They react fast when steam is needed. Water-tube boilers can reach much higher pressures, from 60 to 150 bar. They make superheated steam. They take longer to start, about 30 to 60 minutes. But they keep pressure steady even if demand changes. Water-tube boilers need good water treatment and skilled workers.
Performance
Performance depends on how well the boiler works, the steam quality, and safety. Water-tube boilers are more efficient, often 5-15% better than fire-tube ones. They have more heating area and less water to heat. They make dry, superheated steam at rates up to 500,000 kg/h. Fire-tube boilers make wet steam, usually at lower rates, up to 20,000 kg/h. It is easier to fix fire-tube boilers. But water-tube boilers are safer because a problem only affects one tube, not the whole tank.

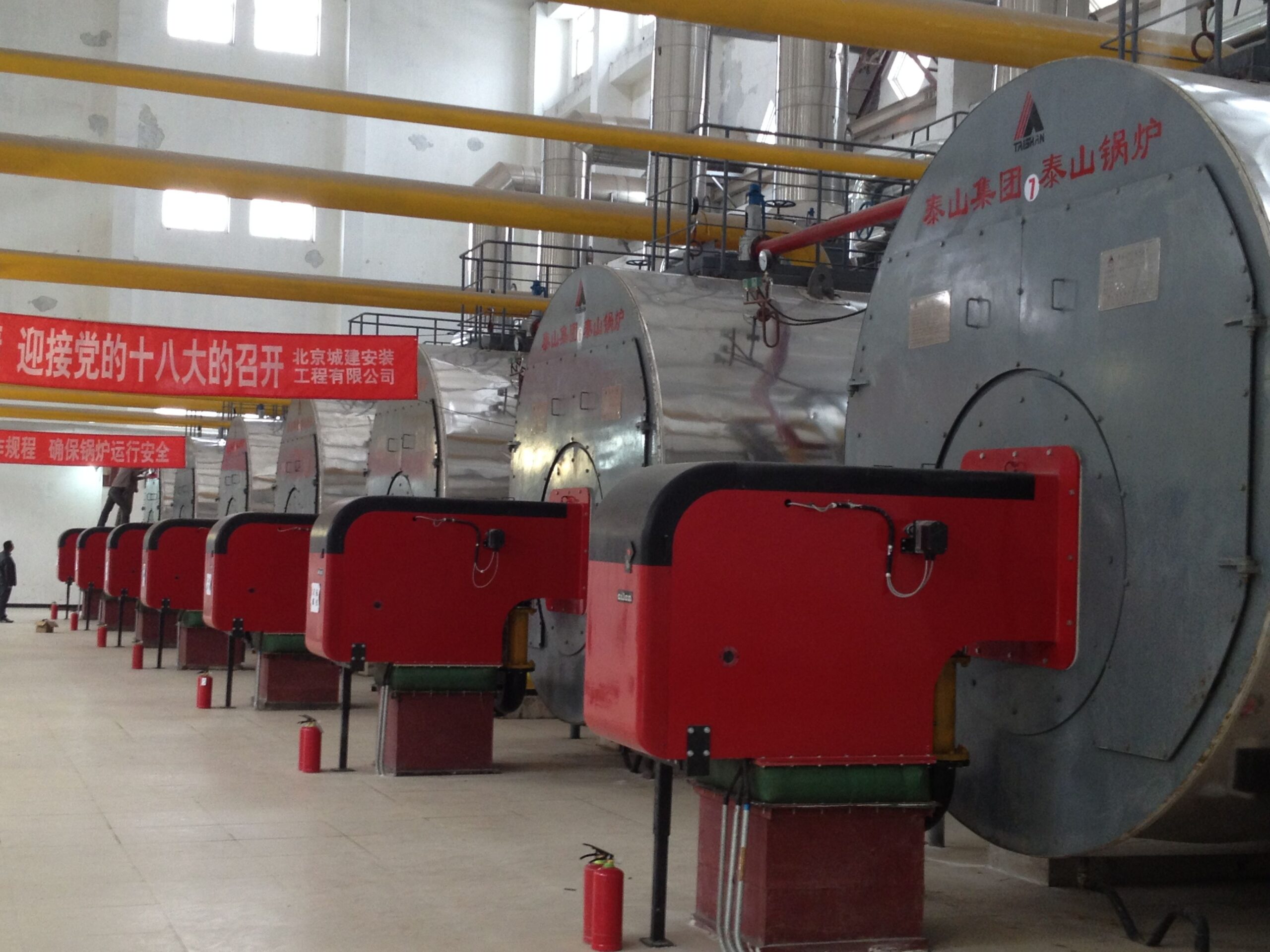
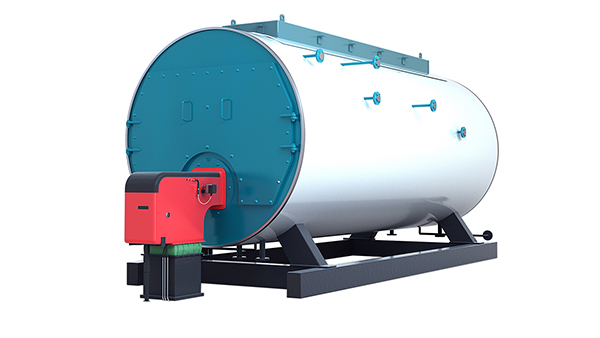
Fire-tube Boilers
How They Work
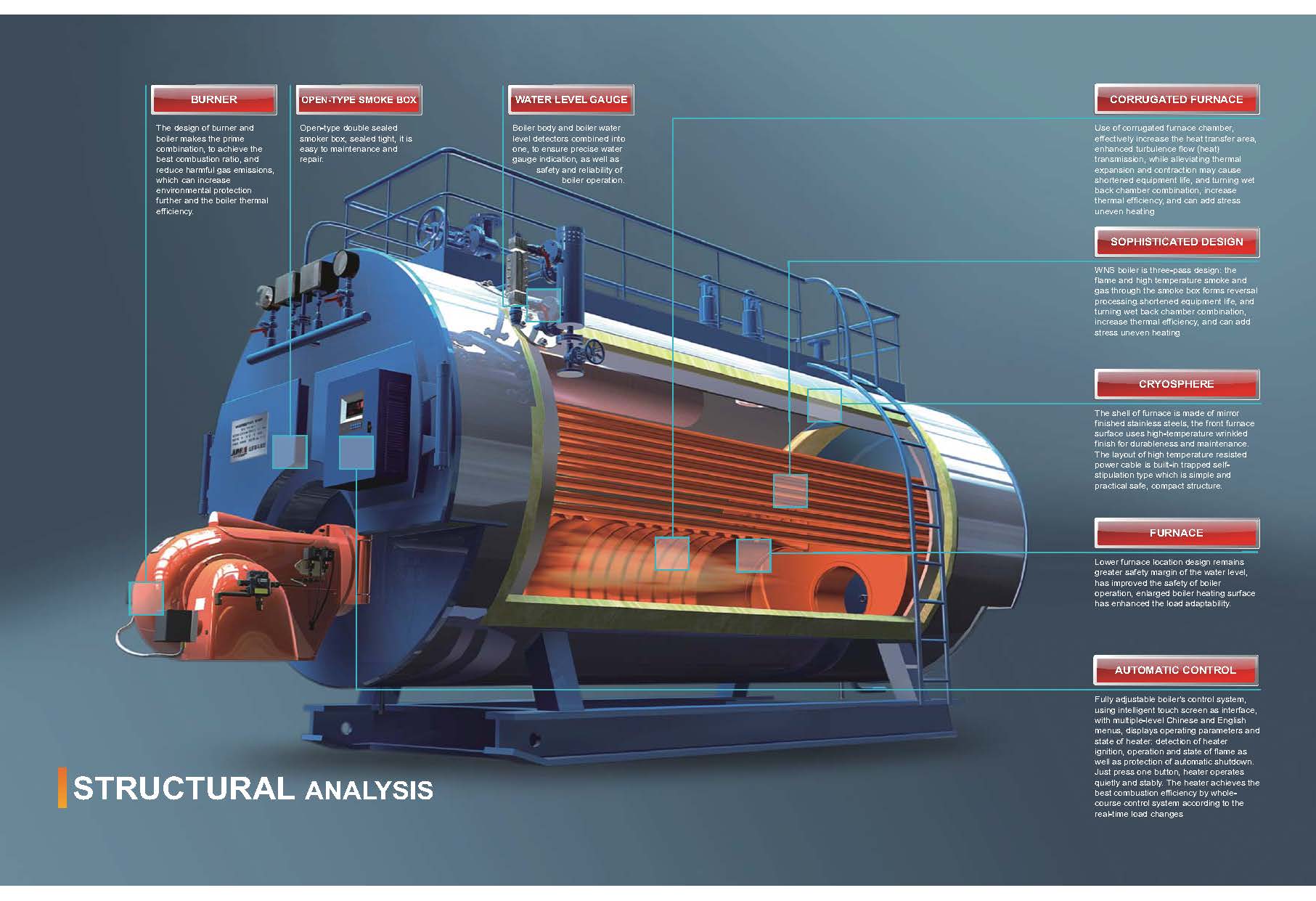
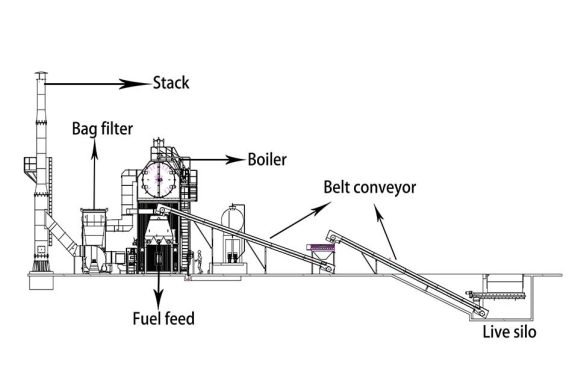
Fire-tube boilers have a simple design. There is a big shell that holds water. Tubes are placed inside this shell. Hot gases from burning fuel move through these tubes. The hot gases heat the water around the tubes. This heat turns the water into steam. Many fire-tube boilers use a multi-pass system. Here, hot gases go through the tubes more than once. This helps the boiler make more steam. It also uses less fuel. Early fire-tube boilers had only one pass. Now, most have two or three passes. These changes help make more steam with less fuel. There are different types of fire-tube boilers. Some are horizontal return tubular, Scotch Marine, and vertical fire-tube. Each type has a special way the tubes and gases move. Fire-tube boilers are used in many places. They are found in sugar mills, textile factories, and chemical plants.
Pros and Cons
Fire-tube boilers have good and bad points. The table below shows some main ones:
Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
Structure & Operation | Simple design, easy to use | Large shell uses more metal |
Maintenance | Low failure rate, easy and low-cost repairs | More damage if a breakdown occurs |
Efficiency | Handles load changes well, safe to operate | Lower pressure and efficiency limits |
Water Capacity | Holds a lot of water | Slow to produce steam |
Feed Water Quality | Works with lower quality water |
|
Fire-tube boilers make steam at pressures below 350 psi. They can make between 500,000 and 75,000,000 BTUs per hour.
The tubes can rust or get weak, but they are easy to change.
Fire-tube boilers cost less money. They fit well in small spaces.
They are easier to use and fix than water-tube boilers.
Tip: Fire-tube boilers are best for small or medium steam needs. They are good when you want simple use.

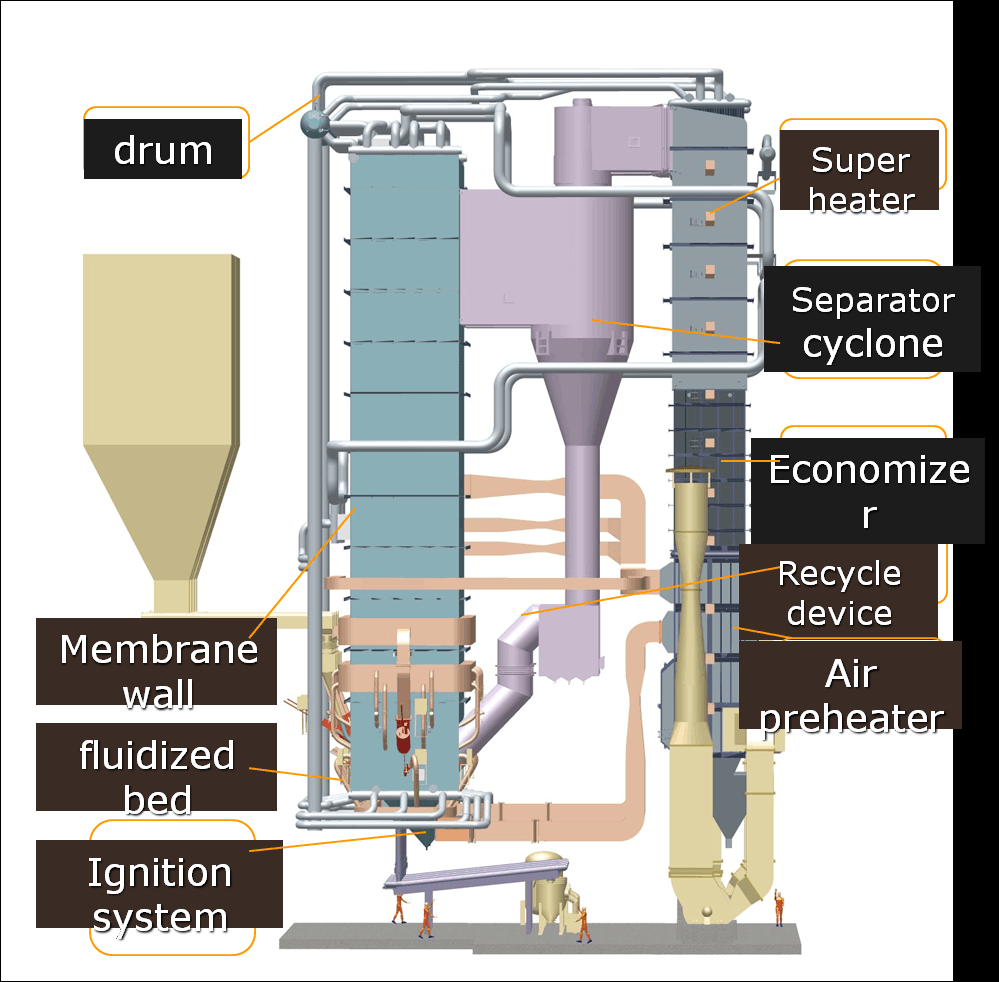
Water-tube Boilers
How They Work
Water-tube boilers are not built like fire-tube boilers. Water moves inside the tubes. Hot gases flow around the tubes. The heat from the gases goes through the tube walls. This heat turns the water into steam. This design lets the boiler handle higher pressure and heat.
Water-tube boilers hold less water. They use two sets of pumps to move water. This keeps the water moving at the right speed. It also helps control the temperature. Operators must watch the water flow all the time. If the water moves too slow, the tubes can get too hot.
Engineers use special tools to make these boilers work better. They add air pre-heaters and economizers to save heat from exhaust gases. Computer models help them set air flow and water temperature. These changes help the boiler use less fuel. Maintenance teams check the system often. They use special tests to find problems early and keep things running.
Note: Small changes in water temperature or air flow can change how well the boiler works. For example, if you raise the water temperature by 10%, the boiler can work about 1% better.
Pros and Cons
The table below lists the main good and bad points of water-tube boilers:
Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Pressure & Temperature | Can reach very high pressures and temperatures | Needs careful water chemistry management |
Efficiency | High efficiency; some models reach up to 98% | Efficiency drops if return water temperature is too high |
Startup & Response | Quick startup and fast response due to low water volume | May need extra water storage to handle sudden demand changes |
Maintenance | Tubes are easy to replace; can last over 40 years | Sensitive to scale buildup; needs steady monitoring |
Fuel & Application | Works with many fuels, including biomass and waste-to-energy | Flexible models are longer and better for smaller capacities |
Cost | Saves 30%-40% on fuel yearly; pays back higher cost in months or years | Condensing models cost 40%-50% more than standard boilers |
Water-tube boilers can use green fuels like biomass.
Checking and fixing the system often keeps it working well.
Even small improvements can save a lot of energy and lower pollution.

Industrial Steam Boiler Comparison
Efficiency
Efficiency is very important when picking an Industrial Steam Boiler. Water-tube boilers are usually more efficient than fire-tube ones. This is because of how they are built. Water-tube boilers have less water inside. They heat up faster and waste less energy. Fire-tube boilers hold more water. They take longer to start and use more fuel to warm up.
Benchmarking lets companies see how well their boilers work. They compare energy use and fuel costs for every 1,000 pounds of steam. This helps managers find ways to save money. For example, a big power plant boiler can reach about 92% efficiency. The steam generation index and fuel use show how much energy is needed for each steam unit. These numbers help companies learn the best ways to save energy.
Water-tube boilers spread heat evenly, so they work better.
Fire-tube boilers can lose efficiency if heat is not spread well.
Even a small 1% boost in efficiency can save a lot of money over time.
Tip: Checking and fixing your boiler often helps it work its best.
Safety
Safety is always very important for Industrial Steam Boilers. Both fire-tube and water-tube boilers must follow strict safety rules. Groups like OSHA and ASME make these rules. Regular checks, training, and good records lower accident risks.
Stress in pipes, bad design, and rust can cause boiler problems.
Water-tube boilers often have better safety features. They have good emission controls and watch systems all the time.
Fire-tube boilers are simpler but can get more damage if something goes wrong.
Tests show water-tube boilers with new fuels can keep emissions safe. Emission controls and regular checks protect workers and the environment.
Note: Clean water and good control systems are needed for safe use in both types.
Cost
Cost is more than just buying the boiler. It also includes setup, fuel, repairs, workers, water treatment, and lost time. For most Industrial Steam Boilers, fuel is about 90% of the total cost over its life.
Fire-tube boilers cost less to buy and set up.
Water-tube boilers cost more at first but save money later. They use less fuel and work more efficiently.
A high-efficiency boiler can pay for itself in less than two years.
Over 20 years, a 1% efficiency gain can save up to $1.5 million.
Some companies use service plans that include repairs and upgrades. This can lower costs and make the boiler more reliable.
Capacity & Pressure
How much steam and pressure you need helps pick the right boiler. Fire-tube boilers are good for lower pressures and smaller steam jobs. Water-tube boilers work for higher pressures and bigger steam needs.
Parameter | Fire-tube Boiler | Water-tube Boiler |
|---|---|---|
Up to 2.5 MPa | Exceeds 2.5 MPa | |
Capacity Threshold | Up to 35 t/h | Above 35 t/h |
Structural Limits | Limited by shell size | Can add superheaters |
Water-tube boilers use thicker shells and special metals for high pressure. They also need better water treatment and certified safety valves. Picking the right steam size and pressure stops waste and damage.
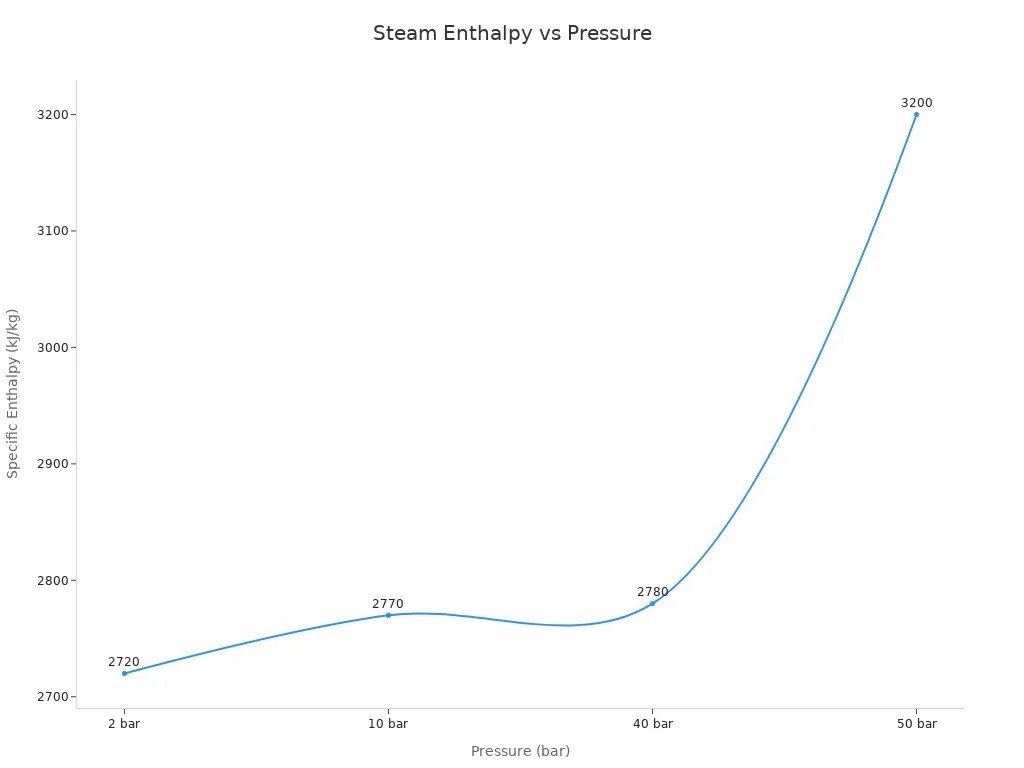
Higher pressure and heat give steam more energy and make the system work better.
Maintenance
Maintenance keeps an Industrial Steam Boiler safe and working well. Both types need regular checks, cleaning, and repairs.
Preventive care means weekly checks, monthly cleaning, and yearly full inspections.
Fire-tube boilers are easier and cheaper to fix. Their simple build lets you change tubes quickly.
Water-tube boilers need skilled workers and careful water treatment. They last longer but need more care to stop scale and rust.
Maintenance costs are $100 to $300 per visit. Repairs can cost up to $1,500 or more.
Computer systems help track checks and repairs, which lowers downtime.
Boilers that are well cared for break down less and last longer.
Applications
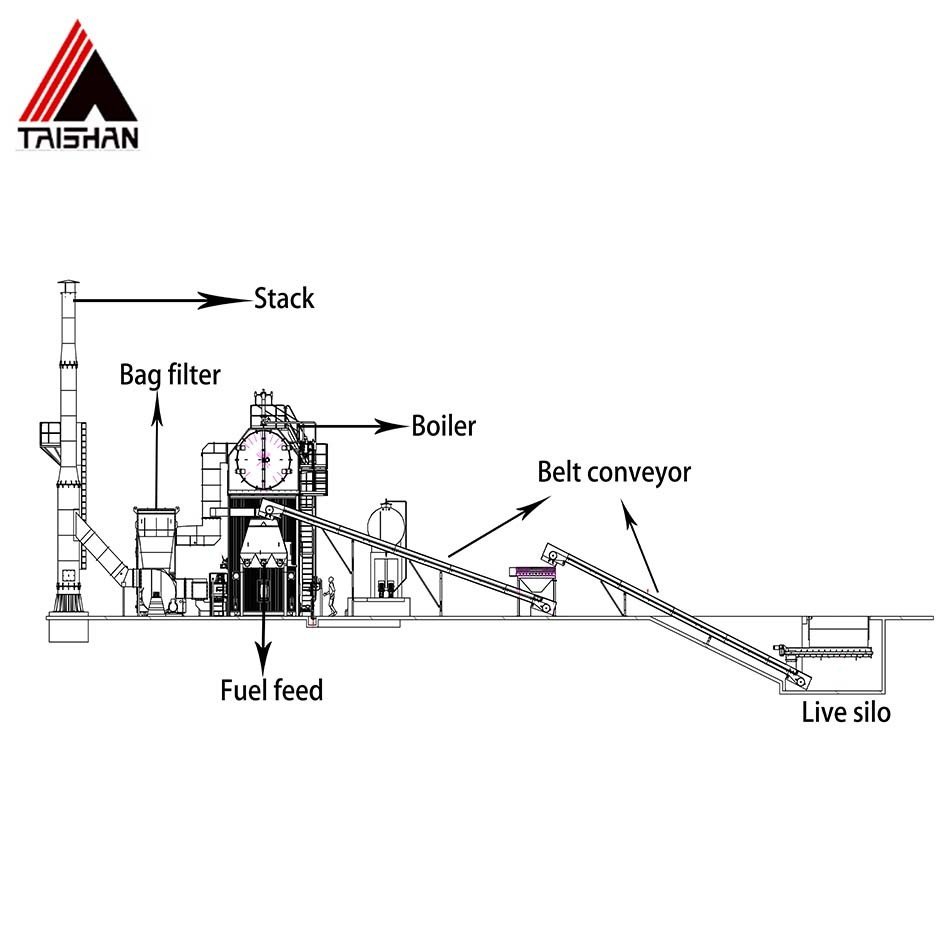
Industrial Steam Boilers are used in many industries. Fire-tube boilers are good for small and medium jobs. These include food processing, textiles, and small factories. Water-tube boilers are used in big plants, refineries, and chemical factories.
Boilers from 10-50 MMBtu/hr are common in chemical, food, and textile jobs.
Smaller boilers are being used more by small businesses and for local energy.
Condensing boilers save energy by using extra heat and meet new rules.
Each industry needs different fuels, emission controls, and steam quality. The best boiler matches these needs with what the system can do.

Choosing a Boiler
Assessing Needs
Picking the right boiler starts with knowing what you need. Facility managers look at how much steam is needed and how much pressure is required. They also check the temperature and how much the load changes each day. They think about what the plant wants to make and how long the boiler should last. They also plan for upgrades in the future. Managers use tools like looking at the boiler, using sound waves to test it, and checking for rust. These steps help them guess how long the old boiler will last. They also check how well the burner works and if safety devices are working. This makes sure the new boiler will work now and later.
Space & Installation
Planning space is important when picking a boiler. Guides say you need at least 3 feet around the boiler to keep it safe and easy to fix. Most boilers take up about 5 by 10 feet. Bigger systems need more room for extra parts like tanks and economizers. Engineers make sure the floor can hold the boiler’s weight. They also check if pipes and wires are ready. Good air flow and a dry, clean room stop damage and keep things safe. Making early drawings helps stop problems with space and saves money.
Budget & Lifecycle
Money planning is more than just buying the boiler. You have to think about the cost to buy it, fuel, water cleaning, fixing it, and taking it out later. The table below shows two boiler choices over 20 years:
Boiler Option | Initial Cost | Annual Fuel Cost | Annual Maintenance | Lifecycle Cost (20 years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Boiler A (Lower Cost) | $150,000 | $75,000 | $7,000 | $2.01 million |
Boiler B (High Efficiency) | $220,000 | $58,000 | $5,000 | $1.74 million |
Managers use fuel price guesses, smart meter numbers, and risk tools to plan for the future. High-efficiency boilers often save enough money to pay for themselves.
Safety & Compliance
Safety is always very important. Regular checks and audits help find problems early and stop breakdowns. Certified inspectors look at safety valves, burners, and control systems. Workers get training on what to do in an emergency and how to use safety devices. Keeping good records of checks and repairs helps with audits and stops fines. Places that follow safety rules have fewer problems and work better.
Application Match
Picking the right boiler for the job helps it work well. For example, a food plant in Ohio saved money by changing how the boiler runs. Chemical plants use data to set the best pressure and temperature. This saves fuel and cuts pollution. Schools and hospitals pick boilers based on steam or hot water needs, fuel type, and how efficient they are. Looking at case studies and data helps managers pick the best Industrial Steam Boiler for their needs.
Fire-tube boilers are easy to use and fix. They work well in small places. Water-tube boilers are better for big jobs. They use less fuel and can handle more pressure. Big factories need these for their work. Experts say every industry has its own rules and needs. For example, food and chemical plants need different heating. Picking the right boiler keeps things safe and saves energy. It also helps follow the rules. Managers should talk to experts before they choose a boiler. They need to check what their building needs.

FAQ
What is the main difference between fire-tube and water-tube boilers?
Fire-tube boilers have hot gases inside tubes. Water surrounds these tubes. Water-tube boilers are different. Water goes inside the tubes. Hot gases move around the tubes. This design changes how much pressure each can handle. It also changes how well they work and what jobs they fit.
Which boiler type is safer for high-pressure applications?
Water-tube boilers are safer for high pressure. Their design keeps problems small if something breaks. Only one tube is affected, not the whole system. This is why people pick them for big jobs with lots of pressure.
How often should industrial steam boilers receive maintenance?
Most experts say to check boilers every week. Clean them once a month. Do a full inspection every year. Doing this helps stop problems before they start. It also keeps the boiler safe and working well.
Can both boiler types use alternative fuels like biomass?
Yes, both types can use other fuels. Water-tube boilers can use more kinds of fuel. They work with things like biomass and waste-to-energy. This is because their design is more flexible.
What factors affect the total cost of owning a boiler?
The total cost includes buying and setting up the boiler. You also pay for fuel, water cleaning, fixing, and lost time if it breaks. High-efficiency boilers cost more at first. But they save money later because they use less fuel and need fewer repairs.

Wade Zhang
Industrial Steam Boiler Choices: Fire-Tube vs. Water-Tube Explained Read More »



















-scaled.jpg)